Humanized-BLT mouse model of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- PMID: 24516154
- PMCID: PMC3939909
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1318175111
Humanized-BLT mouse model of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
Abstract
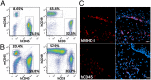
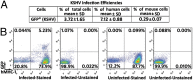
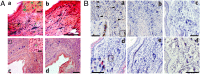
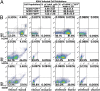
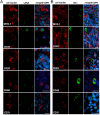
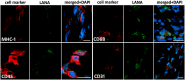
Lack of an effective small-animal model to study the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection in vivo has hampered studies on the pathogenesis and transmission of KSHV. The objective of our study was to determine whether the humanized BLT (bone marrow, liver, and thymus) mouse (hu-BLT) model generated from NOD/SCID/IL2rγ mice can be a useful model for studying KSHV infection. We have tested KSHV infection of hu-BLT mice via various routes of infection, including oral and intravaginal routes, to mimic natural routes of transmission, with recombinant KSHV over a 1- or 3-mo period. Infection was determined by measuring viral DNA, latent and lytic viral transcripts and antigens in various tissues by PCR, in situ hybridization, and immunohistochemical staining. KSHV DNA, as well as both latent and lytic viral transcripts and proteins, were detected in various tissues, via various routes of infection. Using double-labeled immune-fluorescence confocal microscopy, we found that KSHV can establish infection in human B cells and macrophages. Our results demonstrate that KSHV can establish a robust infection in the hu-BLT mice, via different routes of infection, including the oral mucosa which is the most common natural route of infection. This hu-BLT mouse not only will be a useful model for studying the pathogenesis of KSHV in vivo but can potentially be used to study the routes and spread of viral infection in the infected host.
Keywords: HHV-8; humanized mice; mucosa transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-human primate model of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000606. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000606. Epub 2009 Oct 2. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19798430 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8 infection in reactive lymphoid tissues: a model for KSHV/HHV-8-related lymphomas?Hum Pathol. 2006 Jan;37(1):23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2005.08.020. Hum Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16360412
-
Intrafamiliar transmission of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and seronegative infection in family members of classic Kaposi's sarcoma patients.J Gen Virol. 2011 Apr;92(Pt 4):744-51. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.027847-0. Epub 2011 Jan 7. J Gen Virol. 2011. PMID: 21216985
-
Pathological Features of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1045:357-376. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7230-7_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29896675 Review.
-
[Replication Machinery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and Drug Discovery Research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):69-73. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00164-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606932 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Tenofovir alafenamide and elvitegravir loaded nanoparticles for long-acting prevention of HIV-1 vaginal transmission.AIDS. 2017 Feb 20;31(4):469-476. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001349. AIDS. 2017. PMID: 28121666 Free PMC article.
-
High-fat diet feeding exacerbates HIV-1 rectal transmission.mSystems. 2024 Mar 19;9(3):e0132223. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01322-23. Epub 2024 Feb 2. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38303112 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental co-transmission of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) and the macaque homologs of the Kaposi Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) and Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV).PLoS One. 2018 Nov 16;13(11):e0205632. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205632. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30444879 Free PMC article.
-
Spatially Resolved and Highly Multiplexed Protein and RNA In Situ Detection by Combining CODEX With RNAscope In Situ Hybridization.J Histochem Cytochem. 2022 Aug;70(8):571-581. doi: 10.1369/00221554221114174. Epub 2022 Jul 16. J Histochem Cytochem. 2022. PMID: 35848523 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and innovations in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: exploring bone marrow niches and new model systems.BMB Rep. 2024 Aug;57(8):352-362. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2024-0074. BMB Rep. 2024. PMID: 38919014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antman K, Chang Y. Kaposi’s sarcoma. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(14):1027–1038. - PubMed
-
- Picchio GR, et al. The KSHV/HHV8-infected BCBL-1 lymphoma line causes tumors in SCID mice but fails to transmit virus to a human peripheral blood mononuclear cell graft. Virology. 1997;238(1):22–29. - PubMed
-
- Foreman KE, et al. Injection of human herpesvirus-8 in human skin engrafted on SCID mice induces Kaposi’s sarcoma-like lesions. J Dermatol Sci. 2001;26(3):182–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

