Mitogen-induced B-cell proliferation activates Chk2-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest
- PMID: 24498068
- PMCID: PMC3907503
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087299
Mitogen-induced B-cell proliferation activates Chk2-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest
Abstract
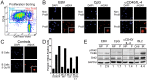
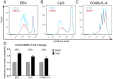
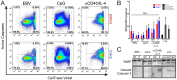
B-cell activation and proliferation can be induced by a variety of extracellular stimuli. The fate of an activated B cell following mitogen stimulation can be dictated by the strength or duration of the signal, the expression of downstream signaling components necessary to promote proliferation, and the cell intrinsic sensors and regulators of the proliferative program. Previously we have identified the DNA damage response (DDR) signaling pathway as a cell intrinsic sensor that is activated upon latent infection of primary human B cells by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Here we have assessed the role of the DDR as a limiting factor in the proliferative response to non-viral B-cell mitogens. We report that TLR9 activation through CpG-rich oligonucleotides induced B-cell hyper-proliferation and an ATM/Chk2 downstream signaling pathway. However, B-cell activation through the CD40 pathway coupled with interleukin-4 (IL-4) promoted proliferation less robustly and only a modest DDR. These two mitogens, but not EBV, modestly induced intrinsic apoptosis that was independent from the DDR. However, all three mitogens triggered a DDR-dependent G1/S phase cell cycle arrest preventing B-cell proliferation. The extent of G1/S arrest, as evidenced by release through Chk2 inhibition, correlated with B-cell proliferation rates. These findings have implications for the regulation of extra-follicular B-cell activation as it may pertain to the development of auto-immune diseases or lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sustained CHK2 activity, but not ATM activity, is critical to maintain a G1 arrest after DNA damage in untransformed cells.BMC Biol. 2021 Feb 19;19(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-00965-x. BMC Biol. 2021. PMID: 33607997 Free PMC article.
-
Rotavirus activates a noncanonical ATM-Chk2 branch of DNA damage response during infection to positively regulate viroplasm dynamics.Cell Microbiol. 2020 Mar;22(3):e13149. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13149. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Cell Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31845505
-
Activation of ATM/Chk2 by Zanthoxylum armatum DC extract induces DNA damage and G1/S phase arrest in BRL 3A cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;284:114832. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114832. Epub 2021 Nov 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34775036
-
An ATM/Chk2-mediated DNA damage-responsive signaling pathway suppresses Epstein-Barr virus transformation of primary human B cells.Cell Host Microbe. 2010 Dec 16;8(6):510-22. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.11.004. Cell Host Microbe. 2010. PMID: 21147465 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage checkpoint kinases in cancer.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2020 Jun 8;22:e2. doi: 10.1017/erm.2020.3. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32508294 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular BH3 Profiling Reveals Shifts in Antiapoptotic Dependency in Human B Cell Maturation and Mitogen-Stimulated Proliferation.J Immunol. 2018 Mar 1;200(5):1727-1736. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701473. Epub 2018 Jan 22. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29358277 Free PMC article.
-
Limited nucleotide pools restrict Epstein-Barr virus-mediated B-cell immortalization.Oncogenesis. 2017 Jun 12;6(6):e349. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2017.46. Oncogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28604764 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals transcriptomic heterogeneity mediated by host-pathogen dynamics in lymphoblastoid cell lines.Elife. 2021 Jan 27;10:e62586. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62586. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33501914 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus reactivation induces divergent abortive, reprogrammed, and host shutoff states by lytic progression.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 24;20(10):e1012341. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012341. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39446925 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of Toll-like receptor 9 signaling in B cell malignancies and its potential therapeutic application.J Transl Med. 2017 Feb 27;15(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1152-5. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28241765 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goodnow CC, Vinuesa CG, Randall KL, Mackay F, Brink R (2010) Control systems and decision making for antibody production. Nat Immunol 11: 681–688. - PubMed
-
- Cahir McFarland ED, Izumi KM, Mosialos G (1999) Epstein-barr virus transformation: involvement of latent membrane protein 1-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Oncogene 18: 6959–6964. - PubMed
-
- Miller CL, Burkhardt AL, Lee JH, Stealey B, Longnecker R, et al. (1995) Integral membrane protein 2 of Epstein-Barr virus regulates reactivation from latency through dominant negative effects on protein-tyrosine kinases. Immunity 2: 155–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

