Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C binds to BATF/IRF4 or SPI1/IRF4 composite sites and recruits Sin3A to repress CDKN2A
- PMID: 24344258
- PMCID: PMC3890834
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1321704111
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C binds to BATF/IRF4 or SPI1/IRF4 composite sites and recruits Sin3A to repress CDKN2A
Abstract
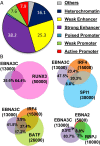
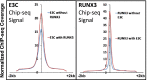
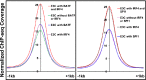
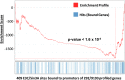
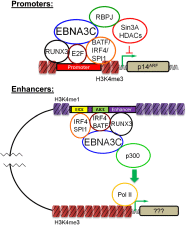
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C (EBNA3C) repression of CDKN2A p14(ARF) and p16(INK4A) is essential for immortal human B-lymphoblastoid cell line (LCL) growth. EBNA3C ChIP-sequencing identified >13,000 EBNA3C sites in LCL DNA. Most EBNA3C sites were associated with active transcription; 64% were strong H3K4me1- and H3K27ac-marked enhancers and 16% were active promoters marked by H3K4me3 and H3K9ac. Using ENCODE LCL transcription factor ChIP-sequencing data, EBNA3C sites coincided (±250 bp) with RUNX3 (64%), BATF (55%), ATF2 (51%), IRF4 (41%), MEF2A (35%), PAX5 (34%), SPI1 (29%), BCL11a (28%), SP1 (26%), TCF12 (23%), NF-κB (23%), POU2F2 (23%), and RBPJ (16%). EBNA3C sites separated into five distinct clusters: (i) Sin3A, (ii) EBNA2/RBPJ, (iii) SPI1, and (iv) strong or (v) weak BATF/IRF4. EBNA3C signals were positively affected by RUNX3, BATF/IRF4 (AICE) and SPI1/IRF4 (EICE) cooccupancy. Gene set enrichment analyses correlated EBNA3C/Sin3A promoter sites with transcription down-regulation (P < 1.6 × 10(-4)). EBNA3C signals were strongest at BATF/IRF4 and SPI1/IRF4 composite sites. EBNA3C bound strongly to the p14(ARF) promoter through SPI1/IRF4/BATF/RUNX3, establishing RBPJ-, Sin3A-, and REST-mediated repression. EBNA3C immune precipitated with Sin3A and conditional EBNA3C inactivation significantly decreased Sin3A binding at the p14(ARF) promoter (P < 0.05). These data support a model in which EBNA3C binds strongly to BATF/IRF4/SPI1/RUNX3 sites to enhance transcription and recruits RBPJ/Sin3A- and REST/NRSF-repressive complexes to repress p14(ARF) and p16(INK4A) expression.
Keywords: EBV; lymphoma; resting B lymphocyte; tumor suppressor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3A partially coincides with EBNA3C genome-wide and is tethered to DNA through BATF complexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 13;112(2):554-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1422580112. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25540416 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3 (EBNA3) Proteins Regulate EBNA2 Binding to Distinct RBPJ Genomic Sites.J Virol. 2015 Dec 30;90(6):2906-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02737-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26719268 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens 3C and 3A maintain lymphoblastoid cell growth by repressing p16INK4A and p14ARF expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 1;108(5):1919-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019599108. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21245331 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Roles of RUNX in B Cell Immortalisation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;962:283-298. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28299664 Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Proteins EBNA3A and EBNA3C Together Induce Expression of the Oncogenic MicroRNA Cluster miR-221/miR-222 and Ablate Expression of Its Target p57KIP2.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jul 8;11(7):e1005031. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005031. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26153983 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus subverts mevalonate and fatty acid pathways to promote infected B-cell proliferation and survival.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Sep 13;15(9):e1008030. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008030. eCollection 2019 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31518366 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA-LP is essential for transforming naïve B cells, and facilitates recruitment of transcription factors to the viral genome.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Feb 20;14(2):e1006890. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006890. eCollection 2018 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29462212 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 Genetic Analysis of Virus-Host Interactions.Viruses. 2018 Jan 30;10(2):55. doi: 10.3390/v10020055. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29385696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3C Facilitates Cell Proliferation by Regulating Cyclin D2.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00663-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00663-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29997218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rickinson A, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Howley P, Knipe D, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2655–2700.
-
- Kieff E, Rickinson A. Epstein-Barr virus and its replication. In: Howley P, Knipe D, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2603–2654.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

