Psy2 targets the PP4 family phosphatase Pph3 to dephosphorylate Mth1 and repress glucose transporter gene expression
- PMID: 24277933
- PMCID: PMC3911506
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00279-13
Psy2 targets the PP4 family phosphatase Pph3 to dephosphorylate Mth1 and repress glucose transporter gene expression
Abstract
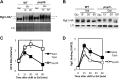
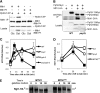
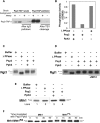
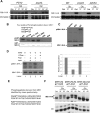
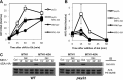
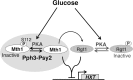
The reversible nature of protein phosphorylation dictates that any protein kinase activity must be counteracted by protein phosphatase activity. How phosphatases target specific phosphoprotein substrates and reverse the action of kinases, however, is poorly understood in a biological context. We address this question by elucidating a novel function of the conserved PP4 family phosphatase Pph3-Psy2, the yeast counterpart of the mammalian PP4c-R3 complex, in the glucose-signaling pathway. Our studies show that Pph3-Psy2 specifically targets the glucose signal transducer protein Mth1 via direct binding of the EVH1 domain of the Psy2 regulatory subunit to the polyproline motif of Mth1. This activity is required for the timely dephosphorylation of the downstream transcriptional repressor Rgt1 upon glucose withdrawal, a critical event in the repression of HXT genes, which encode glucose transporters. Pph3-Psy2 dephosphorylates Mth1, an Rgt1 associated corepressor, but does not dephosphorylate Rgt1 at sites associated with inactivation, in vitro. We show that Pph3-Psy2 phosphatase antagonizes Mth1 phosphorylation by protein kinase A (PKA), the major protein kinase activated in response to glucose, in vitro and regulates Mth1 function via putative PKA phosphorylation sites in vivo. We conclude that the Pph3-Psy2 phosphatase modulates Mth1 activity to facilitate precise regulation of HXT gene expression by glucose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mth1 regulates the interaction between the Rgt1 repressor and the Ssn6-Tup1 corepressor complex by modulating PKA-dependent phosphorylation of Rgt1.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 May;24(9):1493-503. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-01-0047. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23468525 Free PMC article.
-
The repressor Rgt1 and the cAMP-dependent protein kinases control the expression of the SUC2 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1850(7):1362-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25810078
-
How the Rgt1 transcription factor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is regulated by glucose.Genetics. 2005 Feb;169(2):583-94. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034512. Epub 2004 Oct 16. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15489524 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of TOR and PKA Signaling in S. cerevisiae.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 26;12(2):210. doi: 10.3390/biom12020210. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
When Phosphatases Go Mad: The Molecular Basis for Toxicity of Yeast Ppz1.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 13;23(8):4304. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084304. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Robustness of Nutrient Signaling Is Maintained by Interconnectivity Between Signal Transduction Pathways.Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 21;9:1964. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01964. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30719010 Free PMC article.
-
Novel perspectives of target-binding by the evolutionarily conserved PP4 phosphatase.Open Biol. 2020 Dec;10(12):200343. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200343. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 33352067 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK) and protein phosphatases are involved in Aspergillus fumigatus adhesion and biofilm formation.Cell Surf. 2018 Mar 26;1:43-56. doi: 10.1016/j.tcsw.2018.03.002. eCollection 2018 Mar. Cell Surf. 2018. PMID: 32743127 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase 4 (PP4) functions as a critical regulator in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced hepatic insulin resistance.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 15;5:18093. doi: 10.1038/srep18093. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26666849 Free PMC article.
-
Centromeric binding and activity of Protein Phosphatase 4.Nat Commun. 2015 Jan 6;6:5894. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6894. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25562660 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM059441/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA82683/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR011823/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059441/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA80100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK60367-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM043487/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK060367/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM043487/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082683/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
