Interaction with both ZNRF3 and LGR4 is required for the signalling activity of R-spondin
- PMID: 24165923
- PMCID: PMC3981092
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2013.167
Interaction with both ZNRF3 and LGR4 is required for the signalling activity of R-spondin
Abstract
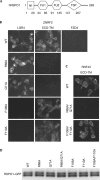
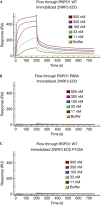
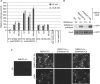
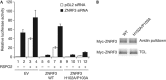
R-spondin proteins sensitize cells to Wnt signalling and act as potent stem cell growth factors. Various membrane proteins have been proposed as potential receptors of R-spondin, including LGR4/5, membrane E3 ubiquitin ligases ZNRF3/RNF43 and several others proteins. Here, we show that R-spondin interacts with ZNRF3/RNF43 and LGR4 through distinct motifs. Both LGR4 and ZNRF3 binding motifs are required for R-spondin-induced LGR4/ZNRF3 interaction, membrane clearance of ZNRF3 and activation of Wnt signalling. Importantly, Wnt-inhibitory activity of ZNRF3, but not of a ZNRF3 mutant with reduced affinity to R-spondin, can be strongly suppressed by R-spondin, suggesting that R-spondin primarily functions by binding and inhibiting ZNRF3. Together, our results support a dual receptor model of R-spondin action, where LGR4/5 serve as the engagement receptor whereas ZNRF3/RNF43 function as the effector receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ZNRF3 promotes Wnt receptor turnover in an R-spondin-sensitive manner.Nature. 2012 Apr 29;485(7397):195-200. doi: 10.1038/nature11019. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22575959
-
LGR4 and LGR5 form distinct homodimers that only LGR4 complexes with RNF43/ZNRF3 to provide high affinity binding of R-spondin ligands.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 4;13(1):10796. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37856-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37402772 Free PMC article.
-
USP42 protects ZNRF3/RNF43 from R-spondin-dependent clearance and inhibits Wnt signalling.EMBO Rep. 2021 May 5;22(5):e51415. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051415. Epub 2021 Mar 30. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33786993 Free PMC article.
-
The R-spondin/Lgr5/Rnf43 module: regulator of Wnt signal strength.Genes Dev. 2014 Feb 15;28(4):305-16. doi: 10.1101/gad.235473.113. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24532711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module in liver homeostasis, regeneration, and disease.Hepatology. 2022 Sep;76(3):888-899. doi: 10.1002/hep.32328. Epub 2022 Feb 20. Hepatology. 2022. PMID: 35006616 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of LGR4 (GPR48) in Normal and Cancer Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4690. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094690. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of R-spondin proteins in cancer biology.Oncogene. 2021 Nov;40(47):6469-6478. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02059-y. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34663878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial cell-derived RSPO3 activates Gαi1/3-Erk signaling and protects neurons from ischemia/reperfusion injury.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Oct 7;14(10):654. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06176-2. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37805583 Free PMC article.
-
Non-equivalence of Wnt and R-spondin ligands during Lgr5+ intestinal stem-cell self-renewal.Nature. 2017 May 11;545(7653):238-242. doi: 10.1038/nature22313. Epub 2017 May 3. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28467820 Free PMC article.
-
A novel function of R-spondin1 in regulating estrogen receptor expression independent of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Elife. 2020 Aug 4;9:e56434. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56434. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32749219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clevers H, Nusse R (2012) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149: 1192–1205 - PubMed
-
- Kazanskaya O, Glinka A, del BBI, Stannek P, Niehrs C, Wu W (2004) R-Spondin2 is a secreted activator of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and is required for Xenopus myogenesis. Dev Cell 7: 525–534 - PubMed
-
- Blaydon DC et al. (2006) The gene encoding R-spondin 4 (RSPO4), a secreted protein implicated in Wnt signaling, is mutated in inherited anonychia. Nat Genet 38: 1245–1247 - PubMed
-
- Kim KA et al. (2005) Mitogenic influence of human R-spondin1 on the intestinal epithelium. Science 309: 1256–1259 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

