αB-crystallin: a novel regulator of breast cancer metastasis to the brain
- PMID: 24132917
- PMCID: PMC3973485
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1255
αB-crystallin: a novel regulator of breast cancer metastasis to the brain
Abstract
Purpose: Basal-like breast tumors are typically (ER/PR/HER2) triple-negative and are associated with a high incidence of brain metastases and poor clinical outcomes. The molecular chaperone αB-crystallin is predominantly expressed in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and contributes to an aggressive tumor phenotype in preclinical models. We investigated the potential role of αB-crystallin in brain metastasis in TNBCs.
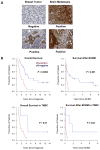
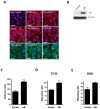
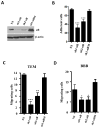
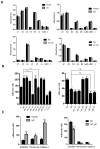
Experimental design: αB-crystallin expression in primary breast carcinomas and brain metastases was analyzed by immunohistochemistry among patients with breast cancer with brain metastases. αB-crystallin was overexpressed or silenced in two different TNBC cell lines. The effects on cell adhesion to human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) or extracellular matrix proteins, transendothelial migration, and transmigration across a HBMEC/astrocyte coculture blood-brain barrier (BBB) model were examined. In addition, the effects of overexpressing or silencing αB-crystallin on brain metastasis in vivo were investigated using orthotopic TNBC models.
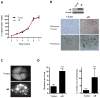
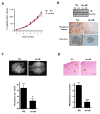
Results: In a cohort of women with breast cancer brain metastasis, αB-crystallin expression in primary breast carcinomas was associated with poor overall survival and poor survival after brain metastasis, even among patients with TNBC. Stable overexpression of αB-crystallin in TNBC cells enhanced adhesion to HBMECs, transendothelial migration, and BBB transmigration in vitro, whereas silencing αB-crystallin inhibited these events. αB-crystallin promoted adhesion of TNBC cells to HBMECs, at least in part, through an α3β1 integrin-dependent mechanism. αB-crystallin overexpression promoted brain metastasis, whereas silencing αB-crystallin inhibited brain metastasis in orthotopic TNBC models.
Conclusion: αB-crystallin is a novel regulator of brain metastasis in TNBC and represents a potential biomarker and drug target for this aggressive disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluorouracil exacerbates alpha-crystallin B chain-mediated cell migration in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 10;13(1):4010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31186-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36899050 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-crystallin B chains enhance cell migration in basal-like 2 triple-negative breast cancer cells.Pharmazie. 2022 Feb 1;77(2):45-47. doi: 10.1691/ph.2022.11019. Pharmazie. 2022. PMID: 35209962
-
αB-crystallin expression is correlated with phospho-ERK1/2 expression in human breast cancer.Int J Biol Markers. 2013 Dec 17;28(4):e365-70. doi: 10.5301/jbm.5000032. Int J Biol Markers. 2013. PMID: 23722303
-
αB-crystallin as a promising target in pathological conditions - A review.Ann Agric Environ Med. 2020 Sep 11;27(3):326-334. doi: 10.26444/aaem/111759. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2020. PMID: 32955210 Review.
-
Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying brain metastasis of breast cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Sep;39(3):711-720. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09881-y. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 32399646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell analysis of breast cancer metastasis reveals epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity signatures associated with poor outcomes.J Clin Invest. 2024 Sep 3;134(17):e164227. doi: 10.1172/JCI164227. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39225101 Free PMC article.
-
Critical functions of extracellular matrix in brain metastasis seeding.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Sep 20;80(10):297. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04944-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37728789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The origin of brain malignancies at the blood-brain barrier.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Sep 9;80(10):282. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04934-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37688612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging translational insights toward precision medicine approaches for brain metastases.Nat Cancer. 2023 Jul;4(7):955-967. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00585-0. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Nat Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37491527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The progress of microenvironment-targeted therapies in brain metastases.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Mar 28;10:1141994. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1141994. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37056723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

