Comparative immunogenicity of HIV-1 gp160, gp140 and gp120 expressed by live attenuated newcastle disease virus vector
- PMID: 24098600
- PMCID: PMC3788131
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078521
Comparative immunogenicity of HIV-1 gp160, gp140 and gp120 expressed by live attenuated newcastle disease virus vector
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(1). doi:10.1371/annotation/670112f8-b4fd-4622-8a8c-203dc647f807
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Comparative immunogenicity of HIV-1 gp160, gp140 and gp120 expressed by live attenuated newcastle disease virus vector.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 14;15(12):e0244046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244046. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33315934 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
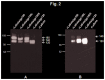
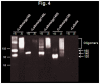
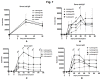
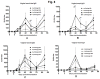
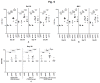
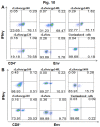
The development of a vaccine against human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) capable of inducing broad humoral and cellular responses at both the systemic and mucosal levels will be critical for combating the global AIDS epidemic. We previously demonstrated the ability of Newcastle disease virus (NDV) as a vaccine vector to express oligomeric Env protein gp160 and induce potent humoral and mucosal immune responses. In the present study, we used NDV vaccine strain LaSota as a vector to compare the biochemical and immunogenic properties of vector-expressed gp160, gp120, and two versions of gp140 (a derivative of gp160 made by deleting the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains), namely: gp140L, which contained the complete membrane-proximal external region (MPER), and gp140S, which lacks the distal half of MPER. We show that, similar to gp160, NDV-expressed gp140S and gp120, but not gp140L, formed higher-order oligomers that retained recognition by conformationally sensitive monoclonal antibodies. Immunization of guinea pigs by the intranasal route with rLaSota/gp140S resulted in significantly greater systemic and mucosal antibody responses compared to the other recombinants. Immunization with rLaSota/140S, rLaSota/140L rLaSota/120 resulted in mixed Th1/Th2 immune responses as compared to Th1-biased immune responses induced by rLaSota/160. Importantly, rLaSota/gp140S induced neutralizing antibody responses to homologous HIV-1 strain BaL.26 and laboratory adapted HIV-1 strain MN.3 that were stronger than those elicited by the other NDV recombinants. Additionally, rLaSota/gp140S induced greater CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses in mice. These studies illustrate that rLaSota/gp140S is a promising vaccine candidate to elicit potent mucosal, humoral and cellular immune responses to the HIV-1 Env protein.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of humoral, mucosal, and cellular immune responses following co-immunization of HIV-1 Gag and Env proteins expressed by Newcastle disease virus.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(2):504-15. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.987006. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25695657 Free PMC article.
-
Newcastle disease virus expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein induces strong mucosal and serum antibody responses in Guinea pigs.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(20):10529-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05050-11. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Virol. 2011. Retraction in: J Virol. 2020 Feb 28;94(6):e01868-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01868-19. PMID: 21849467 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Mucosal Immunization with Newcastle Disease Virus Vector Coexpressing HIV-1 Env and Gag Proteins Elicits Potent Serum, Mucosal, and Cellular Immune Responses That Protect against Vaccinia Virus Env and Gag Challenges.mBio. 2015 Jul 21;6(4):e01005. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01005-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26199332 Free PMC article.
-
[VLP vaccines and effects of HIV-1 Env protein modifications on their antigenic properties].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2016 May-Jun;50(3):406-15. doi: 10.7868/S0026898416030113. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2016. PMID: 27414779 Review. Russian.
-
Novel directions in HIV-1 vaccines revealed from clinical trials.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2013 Sep;8(5):421-31. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e3283632c26. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2013. PMID: 23743791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fusion Proteins CLD and CLDmut Demonstrate Potent and Broad Neutralizing Activity against HIV-1.Viruses. 2022 Jun 23;14(7):1365. doi: 10.3390/v14071365. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891347 Free PMC article.
-
On the irrationality of rational design of an HIV vaccine in light of protein intrinsic disorder.Arch Virol. 2021 May;166(5):1283-1296. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-04984-5. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Arch Virol. 2021. PMID: 33606110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified Newcastle Disease virus as an improved vaccine vector against Simian Immunodeficiency virus.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 12;8(1):8952. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27433-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29895833 Free PMC article.
-
Newcastle disease virus: current status and our understanding.Virus Res. 2014 May 12;184:71-81. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.02.016. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24589707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and Immunogenicity of Two Recombinant Fusion Proteins Comprising Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Structural Protein VP1 and DC-SIGN-Binding Glycoproteins.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7658970. doi: 10.1155/2017/7658970. Epub 2017 Oct 8. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29119112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba TW, Liska V, Hofmann-Lehmann R, Vlasak J, Xu W et al. (2000) Human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies of the IgG1 subtype protect against mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. Nat Med 6: 200-206. doi:10.1038/72309. PubMed: 10655110. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mascola JR, Stiegler G, VanCott TC, Katinger H, Carpenter CB et al. (2000) Protection of macaques against vaginal transmission of a pathogenic HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus by passive infusion of neutralizing antibodies. Nat Med 6: 207-210. doi:10.1038/72318. PubMed: 10655111. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balazs AB, Chen J, Hong CM, Rao DS, Yang L et al. (2012) Antibody-based protection against HIV infection by vectored immunoprophylaxis. Nature 481: 81-84. doi:10.1038/nature10660. PubMed: 22139420. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barouch DH, Liu J, Peter L, Abbink P, Iampietro MJ et al. (2013) Characterization of Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses Elicited by a Recombinant Adenovirus Serotype 26 HIV-1 Env Vaccine in Healthy Adults (IPCAVD 001). J Infect Dis 207: 248-256. doi:10.1093/infdis/jis671. PubMed: 23125443. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Souza MS, Ratto-Kim S, Chuenarom W, Schuetz A, Chantakulkij S et al. (2012) The Thai phase III trial (RV144) vaccine regimen induces T cell responses that preferentially target epitopes within the V2 region of HIV-1 envelope. J Immunol 188: 5166-5176. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102756. PubMed: 22529301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

