Matrine Inhibits Infiltration of the Inflammatory Gr1(hi) Monocyte Subset in Injured Mouse Liver through Inhibition of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1
- PMID: 24058371
- PMCID: PMC3766592
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/580673
Matrine Inhibits Infiltration of the Inflammatory Gr1(hi) Monocyte Subset in Injured Mouse Liver through Inhibition of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1
Abstract
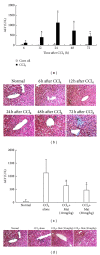
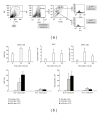
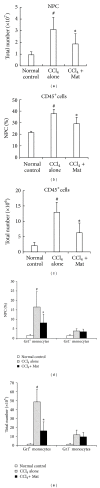
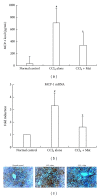
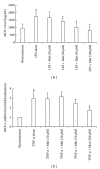
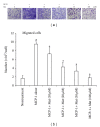
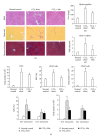
Matrine (Mat) is a major alkaloid extracted from Sophora flavescens Ait, an herb which is used in the traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of inflammation, cancer, and other diseases. The present study examined the impact of Mat on the CCl4-induced hepatic infiltration of Gr1(hi) monocytes to explore the possible mechanisms underlying its anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects. The results indicated that Mat protected mice from acute liver injury induced by single intraperitoneal injection of CCl4 and attenuated liver fibrosis induced by repeated CCl4 injection. Meanwhile, the infiltrations of Gr1(hi) monocytes in both acute and chronic injured livers were all inhibited, and the enhanced hepatic expression of MCP-1 was suppressed. Cellular experiments demonstrated that Mat directly inhibited MCP-1 production in both nonparenchymal cells and hepatic stellate cells derived from CCl4-injured livers. Transwell chemotaxis assays showed that Mat significantly inhibited the chemotactic activity of MCP-1. These results suggest that the anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects of Mat could be contributed, at least in part, to its prevention of Gr1(hi) monocyte infiltration into the injured livers and inhibition of MCP-1 production and activity. These findings extend our understanding of the mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects of Mat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Matrine Derivate MASM Inhibits Recruitment of Gr1hi Monocyte and Alleviates Liver Injury.Pharmacology. 2019;104(5-6):235-243. doi: 10.1159/000501384. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Pharmacology. 2019. PMID: 31357205
-
Emodin Alleviates Liver Fibrosis of Mice by Reducing Infiltration of Gr1hi Monocytes.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Mar 21;2018:5738101. doi: 10.1155/2018/5738101. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29743924 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic recruitment of the inflammatory Gr1+ monocyte subset upon liver injury promotes hepatic fibrosis.Hepatology. 2009 Jul;50(1):261-74. doi: 10.1002/hep.22950. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19554540
-
Monocytes and macrophages as cellular targets in liver fibrosis.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009 Sep;8(4):307-18. doi: 10.2174/187152809789352230. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19534673 Review.
-
Macrophage heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis.J Hepatol. 2014 May;60(5):1090-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.12.025. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24412603 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of the Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmacokinetics of Matrine.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 16;11:01067. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01067. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33041782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrine prevents the early development of hepatocellular carcinoma like lesions in rat liver.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Oct;18(4):2583-2591. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7875. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31555367 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic equilibrium between the protective and toxic effects of matrine in the development of liver injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1315584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1315584. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38348397 Free PMC article.
-
WM130 preferentially inhibits hepatic cancer stem-like cells by suppressing AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):79544-79556. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12822. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27783993 Free PMC article.
-
The Pharmacological Targets and Clinical Evidence of Natural Products With Anti-hepatic Inflammatory Properties.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jun 5;9:455. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00455. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29922155 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Friedman SL. Liver fibrosis—from bench to bedside. Journal of Hepatology, Supplement. 2003;38(1):S38–S53. - PubMed
-
- Winwood PJ, Arthur MJP. Kupffer cells: Their activation and role in animal models of liver injury and human liver disease. Seminars in Liver Disease. 1993;13(1):50–59. - PubMed
-
- Shiratori Y, Geerts A, Ichida T. Kupffer cells from CCl4-induced fibrotic livers stimulate proliferation of fat-storing cells. Journal of Hepatology. 1986;3(3):294–303. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

