Xanthine oxidoreductase-catalyzed reactive species generation: A process in critical need of reevaluation
- PMID: 24024171
- PMCID: PMC3757702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.05.002
Xanthine oxidoreductase-catalyzed reactive species generation: A process in critical need of reevaluation
Abstract
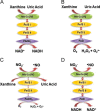
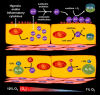
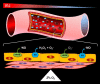
Nearly 30 years have passed since the discovery of xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR) as a critical source of reactive species in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Since then, numerous inflammatory disease processes have been associated with elevated XOR activity and allied reactive species formation solidifying the ideology that enhancement of XOR activity equates to negative clinical outcomes. However, recent evidence may shatter this paradigm by describing a nitrate/nitrite reductase capacity for XOR whereby XOR may be considered a crucial source of beneficial (•)NO under ischemic/hypoxic/acidic conditions; settings similar to those that limit the functional capacity of nitric oxide synthase. Herein, we review XOR-catalyzed reactive species generation and identify key microenvironmental factors whose interplay impacts the identity of the reactive species (oxidants vs. (•)NO) produced. In doing so, we redefine existing dogma and shed new light on an enzyme that has weathered the evolutionary process not as gadfly but a crucial component in the maintenance of homeostasis.
Keywords: Free radicals; GAGs, glycosaminoglycans; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; Hypoxia; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; Inflammation; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; Nitric oxide; Nitrite; O2•−, superoxide; Oxygen tension; ROS, reactive oxygen species; XDH, xanthine dehydrogenase; XO, xanthine oxidase; XOR, xanthine oxidoreductase); Xanthine oxidoreductase; •NO, nitric oxide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Xanthine oxidoreductase-catalyzed reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide: insights regarding where, when and how.Nitric Oxide. 2013 Nov 1;34:19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2013.02.081. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Nitric Oxide. 2013. PMID: 23454592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dispelling dogma and misconceptions regarding the most pharmacologically targetable source of reactive species in inflammatory disease, xanthine oxidoreductase.Arch Toxicol. 2015 Aug;89(8):1193-207. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1523-8. Epub 2015 May 21. Arch Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25995007 Review.
-
A new paradigm for XOR-catalyzed reactive species generation in the endothelium.Pharmacol Rep. 2015 Aug;67(4):669-74. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 23. Pharmacol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26321266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced XOR activity in eNOS-deficient mice: Effects on the nitrate-nitrite-NO pathway and ROS homeostasis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Oct;99:472-484. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27609225
-
Human and rodent red blood cells do not demonstrate xanthine oxidase activity or XO-catalyzed nitrite reduction to NO.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Oct;174:84-88. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.07.012. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34273539 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Loss of cAMP-dependent stimulation of isolated cilia motility by alcohol exposure is oxidant-dependent.Alcohol. 2019 Nov;80:91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 30291947 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition as a Potential Treatment for Aortic Stiffness in Hypertension.Am J Hypertens. 2019 Feb 12;32(3):234-236. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpy197. Am J Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 30561498 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Myeloperoxidase and related biomarkers are suggestive footprints of endothelial microvascular inflammation in HFpEF patients.ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Aug;7(4):1534-1546. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12700. Epub 2020 May 19. ESC Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 32424988 Free PMC article.
-
Linking uric acid metabolism to diabetic complications.World J Diabetes. 2014 Dec 15;5(6):787-95. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i6.787. World J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 25512781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitrite reduction by molybdoenzymes: a new class of nitric oxide-forming nitrite reductases.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015 Mar;20(2):403-33. doi: 10.1007/s00775-014-1234-2. Epub 2015 Jan 15. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015. PMID: 25589250 Review.
References
-
- Nishino T., Okamoto K. The role of the [2Fe–2s] cluster centers in xanthine oxidoreductase. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry. 2000;82:43–49. - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki T., Okamoto K., Nishino T., Mizushima J., Hori H. Sequence motif-specific assignment of two [2Fe–2S] clusters in rat xanthine oxidoreductase studied by site-directed mutagenesis. Journal of Biochemistry. 2000;127:771–778. - PubMed
-
- Harris C.M., Massey V. The oxidative half-reaction of xanthine dehydrogenase with NAD; reaction kinetics and steady-state mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272:28335–28341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

