miR-26a suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting FGF9 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 24015269
- PMCID: PMC3756000
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072662
miR-26a suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting FGF9 in gastric cancer
Abstract
The role of miR-26a in cancer cells seemed controversial in previous studies. Until now, the role of miR-26a in gastric cancer remains undefined. In this study, we found that miR-26a was strongly downregulated in gastric cancer (GC) tissues and cell lines, and its expression levels were associated with lymph node metastasis and clinical stage, as well as overall survival and replase-free survival of GC. We also found that ectopic expression of miR-26a inhibited GC cell proliferation and GC metastasis in vitro and in vivo. We further identified a novel mechanism of miR-26a to suppress GC growth and metastasis. FGF9 was proved to be a direct target of miR-26a, using luciferase assay and western blot. FGF9 overexpression in miR-26a-expressing cells could rescue invasion and growth defects of miR-26a. In addition, miR-26a expression inversely correlated with FGF9 protein levels in GC. Taken together, our data suggest that miR-26a functions as a tumor suppressor in GC development and progression, and holds promise as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for GC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
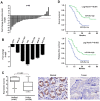
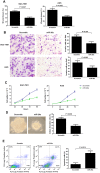
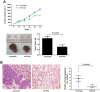
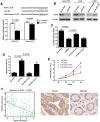
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of miRNA-214 in cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through targeting FGF9 and inducing EMT.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 15;38(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0995-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30646925 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-665 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and inhibits proliferation, invasion, and EMT by targeting PPP2R2A.Cell Biochem Funct. 2020 Jun;38(4):409-418. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3485. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020. PMID: 31923339
-
MicroRNA-365 inhibits growth, invasion and metastasis of malignant melanoma by targeting NRP1 expression.Cancer Biomark. 2015;15(5):599-608. doi: 10.3233/CBM-150500. Cancer Biomark. 2015. PMID: 26406949
-
TGF-β induces HLA-G expression through inhibiting miR-152 in gastric cancer cells.J Biomed Sci. 2015 Dec 2;22:107. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0177-4. J Biomed Sci. 2015. PMID: 26627200 Free PMC article.
-
miR-4317 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by targeting fibroblast growth factor 9 (FGF9) and cyclin D2 (CCND2).J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 18;37(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0882-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30227870 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
FGF9 from cancer-associated fibroblasts is a possible mediator of invasion and anti-apoptosis of gastric cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2015 Apr 30;15:333. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1353-3. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25925261 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNA-26a in human cancer progression and clinical application.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7095-108. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5017-y. Epub 2016 Apr 2. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27039398 Review.
-
MicroRNA-26a regulates ANXA1, rather than DAL-1, in the development of lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):5893-5902. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8048. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29552220 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Cellular Arrangement in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines TOV-21G and SKOV-3 is Associated with Apoptosis-Related miRNA Expression Modulation.Cancer Microenviron. 2018 Jun;11(1):85-92. doi: 10.1007/s12307-017-0203-z. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Cancer Microenviron. 2018. PMID: 29307001 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Cancer Effect of Cordycepin on FGF9-Induced Testicular Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 6;21(21):8336. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218336. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33172093 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

