Epigenetic control of Epstein-Barr virus transcription - relevance to viral life cycle?
- PMID: 23986773
- PMCID: PMC3753449
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00161
Epigenetic control of Epstein-Barr virus transcription - relevance to viral life cycle?
Abstract
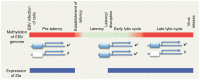
DNA methylation normally leads to silencing of gene expression but Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) provides an exception to the epigenetic paradigm. DNA methylation is absolutely required for the expression of many viral genes. Although the viral genome is initially un-methylated in newly infected cells, it becomes extensively methylated during the establishment of viral latency. One of the major regulators of EBV gene expression is a viral transcription factor called Zta (BZLF1, ZEBRA, Z) that resembles the cellular AP1 transcription factor. Zta recognizes at least 32 variants of a 7-nucleotide DNA sequence element, the Zta-response element (ZRE), some of which contain a CpG motif. Zta only binds to the latter class of ZREs in their DNA-methylated form, whether they occur in viral or cellular promoters and is functionally relevant for the activity of these promoters. The ability of Zta to interpret the differential DNA methylation of the viral genome is paramount for both the establishment of viral latency and the release from latency to initiate viral replication.
Keywords: CpG-DNA methylation; DNA binding; Epstein–Barr virus; cancer; replication cycle; transcription factor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analyses of Zta binding to the Epstein-Barr virus genome reveals interactions in both early and late lytic cycles and an epigenetic switch leading to an altered binding profile.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(23):12494-502. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01705-12. Epub 2012 Sep 26. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 23015699 Free PMC article.
-
CpG-methylation regulates a class of Epstein-Barr virus promoters.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Sep 23;6(9):e1001114. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001114. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20886097 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a prediction protocol to identify potential targets of epigenetic reprogramming by the cancer associated Epstein Barr virus.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 26;5(2):e9443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009443. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20195470 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cellular and viral protein expression by the Epstein-Barr virus transcriptional regulator Zta: implications for therapy of EBV associated tumors.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Jun;8(11):987-95. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.11.8369. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19448399 Review.
-
Could Changing the DNA Methylation Landscape Promote the Destruction of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Cancers?Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 May 28;11:695093. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.695093. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34123880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EBV and Apoptosis: The Viral Master Regulator of Cell Fate?Viruses. 2017 Nov 13;9(11):339. doi: 10.3390/v9110339. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29137176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Plasticity Enables CNS-Trafficking of EBV-infected B Lymphocytes.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jun 9;17(6):e1009618. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009618. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34106998 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics and animal virus infections.Front Genet. 2015 Mar 4;6:48. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00048. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25788901 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mechanism of activation of the BNLF2a immune evasion gene of Epstein-Barr virus by Zta.J Gen Virol. 2018 Jun;99(6):805-817. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001056. Epub 2018 Mar 26. J Gen Virol. 2018. PMID: 29580369 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome, the Constitutive Heterochromatin Machinery, and Replication of an Oncogenic Herpesvirus.Viruses. 2021 May 6;13(5):846. doi: 10.3390/v13050846. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34066537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

