Oncogenic ETS fusions deregulate E2F3 target genes in Ewing sarcoma and prostate cancer
- PMID: 23940108
- PMCID: PMC3814880
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.151340.112
Oncogenic ETS fusions deregulate E2F3 target genes in Ewing sarcoma and prostate cancer
Abstract
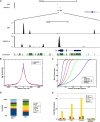
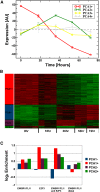
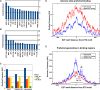
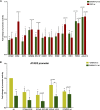
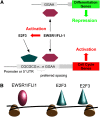
Deregulated E2F transcription factor activity occurs in the vast majority of human tumors and has been solidly implicated in disturbances of cell cycle control, proliferation, and apoptosis. Aberrant E2F regulatory activity is often caused by impairment of control through pRB function, but little is known about the interplay of other oncoproteins with E2F. Here we show that ETS transcription factor fusions resulting from disease driving rearrangements in Ewing sarcoma (ES) and prostate cancer (PC) are one such class of oncoproteins. We performed an integrative study of genome-wide DNA-binding and transcription data in EWSR1/FLI1 expressing ES and TMPRSS2/ERG containing PC cells. Supported by promoter activity and mutation analyses, we demonstrate that a large fraction of E2F3 target genes are synergistically coregulated by these aberrant ETS proteins. We propose that the oncogenic effect of ETS fusion oncoproteins is in part mediated by the disruptive effect of the E2F-ETS interaction on cell cycle control. Additionally, a detailed analysis of the regulatory targets of the characteristic EWSR1/FLI1 fusion in ES identifies two functionally distinct gene sets. While synergistic regulation in concert with E2F in the promoter of target genes has a generally activating effect, EWSR1/FLI1 binding independent of E2F3 is predominantly associated with repressed differentiation genes. Thus, EWSR1/FLI1 appears to promote oncogenesis by simultaneously promoting cell proliferation and perturbing differentiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EWS-FLI1 employs an E2F switch to drive target gene expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Mar 11;43(5):2780-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv123. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25712098 Free PMC article.
-
Potential downstream target genes of aberrant ETS transcription factors are differentially affected in Ewing's sarcoma and prostate carcinoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049819. Epub 2012 Nov 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185447 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput RNAi screen in Ewing sarcoma cells identifies leucine rich repeats and WD repeat domain containing 1 (LRWD1) as a regulator of EWS-FLI1 driven cell viability.Gene. 2017 Jan 5;596:137-146. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.10.021. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Gene. 2017. PMID: 27760381
-
Blocking the road, stopping the engine or killing the driver? Advances in targeting EWS/FLI-1 fusion in Ewing sarcoma as novel therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Nov;18(11):1315-28. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.947963. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 25162919 Review.
-
EWS/FLI1 Characterization, Activation, Repression, Target Genes and Therapeutic Opportunities in Ewing Sarcoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 14;24(20):15173. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015173. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ceramide-induced cleavage of GPR64 intracellular domain drives Ewing sarcoma.Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 27;43(8):114497. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114497. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39024100 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in sequencing and omics studies in prostate cancer: unveiling molecular pathogenesis and clinical applications.Front Oncol. 2024 May 10;14:1355551. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1355551. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38800374 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic ETS fusions promote DNA damage and proinflammatory responses via pericentromeric RNAs in extracellular vesicles.J Clin Invest. 2024 Mar 26;134(9):e169470. doi: 10.1172/JCI169470. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38530366 Free PMC article.
-
SilenceREIN: seeking silencers on anchors of chromatin loops by deep graph neural networks.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Nov 22;25(1):bbad494. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad494. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 38168841 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-495: a therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker.J Mol Histol. 2023 Dec;54(6):559-578. doi: 10.1007/s10735-023-10159-0. Epub 2023 Sep 28. J Mol Histol. 2023. PMID: 37759132 Review.
References
-
- Clark JP, Cooper CS 2009. ETS gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 6: 429–439 - PubMed
-
- Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B, Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M, Kovar H, Joubert I, De Jong P, Rouleau G 1992. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature 359: 162–165 - PubMed
-
- Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC, Lempicki RA 2003. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol 4: 3 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- SRA/SRA096176
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
