Reductive glutamine metabolism is a function of the α-ketoglutarate to citrate ratio in cells
- PMID: 23900562
- PMCID: PMC3934748
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3236
Reductive glutamine metabolism is a function of the α-ketoglutarate to citrate ratio in cells
Abstract
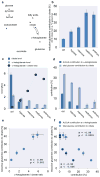
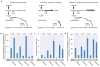
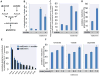
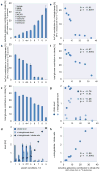
Reductively metabolized glutamine is a major cellular carbon source for fatty acid synthesis during hypoxia or when mitochondrial respiration is impaired. Yet, a mechanistic understanding of what determines reductive metabolism is missing. Here we identify several cellular conditions where the α-ketoglutarate/citrate ratio is changed due to an altered acetyl-CoA to citrate conversion, and demonstrate that reductive glutamine metabolism is initiated in response to perturbations that result in an increase in the α-ketoglutarate/citrate ratio. Thus, targeting reductive glutamine conversion for a therapeutic benefit might require distinct modulations of metabolite concentrations rather than targeting the upstream signalling, which only indirectly affects the process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hypoxia promotes isocitrate dehydrogenase-dependent carboxylation of α-ketoglutarate to citrate to support cell growth and viability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 6;108(49):19611-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1117773108. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22106302 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid labeling from glutamine in hypoxia can be explained by isotope exchange without net reductive isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) flux.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 25;288(43):31363-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.502740. Epub 2013 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24030823 Free PMC article.
-
Reductive glutamine metabolism by IDH1 mediates lipogenesis under hypoxia.Nature. 2011 Nov 20;481(7381):380-4. doi: 10.1038/nature10602. Nature. 2011. PMID: 22101433 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and mind shifts: from glucose to glutamine and acetate addictions in cancer.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015 Jul;18(4):346-53. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000178. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015. PMID: 26001655 Review.
-
Viral effects on metabolism: changes in glucose and glutamine utilization during human cytomegalovirus infection.Trends Microbiol. 2011 Jul;19(7):360-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2011.04.002. Epub 2011 May 12. Trends Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21570293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell cycle progression is regulated by intertwined redox oscillators.Theor Biol Med Model. 2015 May 29;12:10. doi: 10.1186/s12976-015-0005-2. Theor Biol Med Model. 2015. PMID: 26022743 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate from the tumor microenvironment - A key obstacle in NK cell-based immunotherapies.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 18;13:932055. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.932055. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36330529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Independent Effects of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Transaminase (GABAT) on Metabolic and Sleep Homeostasis.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 14;290(33):20407-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.602276. Epub 2015 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26124278 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in brain tumor glutamine metabolism reveal sex-specific vulnerabilities to treatment.Med. 2022 Nov 11;3(11):792-811.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2022.08.005. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Med. 2022. PMID: 36108629 Free PMC article.
-
Altered metabolite levels in cancer: implications for tumour biology and cancer therapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2016 Nov;16(11):680-693. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.85. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27658530 Review.
References
-
- Lunt SY, Vander Heiden MG. Aerobic Glycolysis: Meeting the Metabolic Requirements of Cell Proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:441–464. - PubMed
-
- Daye D, Wellen KE. Metabolic reprogramming in cancer: Unraveling the role of glutamine in tumorigenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012;23(4):362–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

