Transcriptional regulation of human DNA repair genes following genotoxic stress: trigger mechanisms, inducible responses and genotoxic adaptation
- PMID: 23892398
- PMCID: PMC3794595
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt635
Transcriptional regulation of human DNA repair genes following genotoxic stress: trigger mechanisms, inducible responses and genotoxic adaptation
Abstract
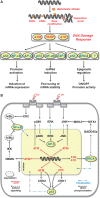
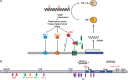
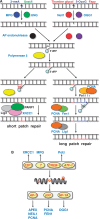
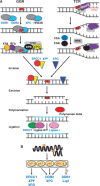
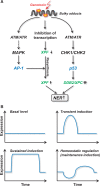
DNA repair is the first barrier in the defense against genotoxic stress. In recent years, mechanisms that recognize DNA damage and activate DNA repair functions through transcriptional upregulation and post-translational modification were the focus of intensive research. Most DNA repair pathways are complex, involving many proteins working in discrete consecutive steps. Therefore, their balanced expression is important for avoiding erroneous repair that might result from excessive base removal and DNA cleavage. Amelioration of DNA repair requires both a fine-tuned system of lesion recognition and transcription factors that regulate repair genes in a balanced way. Transcriptional upregulation of DNA repair genes by genotoxic stress is counteracted by DNA damage that blocks transcription. Therefore, induction of DNA repair resulting in an adaptive response is only visible through a narrow window of dose. Here, we review transcriptional regulation of DNA repair genes in normal and cancer cells and describe mechanisms of promoter activation following genotoxic exposures through environmental carcinogens and anticancer drugs. The data available to date indicate that 25 DNA repair genes are subject to regulation following genotoxic stress in rodent and human cells, but for only a few of them, the data are solid as to the mechanism, homeostatic regulation and involvement in an adaptive response to genotoxic stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genotoxic thresholds, DNA repair, and susceptibility in human populations.Toxicology. 2010 Dec 30;278(3):305-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2009.11.016. Epub 2009 Nov 22. Toxicology. 2010. PMID: 19932733 Review.
-
The egr-1 gene is induced by DNA-damaging agents and non-genotoxic drugs in both normal and neoplastic human cells.Life Sci. 2003 May 16;72(26):2975-92. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(03)00230-3. Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 12706485
-
Human three prime exonuclease TREX1 is induced by genotoxic stress and involved in protection of glioma and melanoma cells to anticancer drugs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1833(8):1832-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.03.029. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23578789
-
APE/Ref-1 and the mammalian response to genotoxic stress.Toxicology. 2003 Nov 15;193(1-2):67-78. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(03)00290-7. Toxicology. 2003. PMID: 14599768 Review.
-
Three prime exonuclease I (TREX1) is Fos/AP-1 regulated by genotoxic stress and protects against ultraviolet light and benzo(a)pyrene-induced DNA damage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6418-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq455. Epub 2010 May 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20511593 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcript Expression Profiles and MicroRNA Regulation Indicate an Upregulation of Processes Linked to Oxidative Stress, DNA Repair, Cell Death, and Inflammation in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.J Diabetes Res. 2022 Feb 1;2022:3511329. doi: 10.1155/2022/3511329. eCollection 2022. J Diabetes Res. 2022. PMID: 35155683 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic Outcomes of Glyphosate Exposure: From Organ Damage to Effects on Inflammation, Cancer, Reproduction and Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12606. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212606. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimal role of base excision repair in TET-induced global DNA demethylation in HEK293T cells.Epigenetics. 2015;10(11):1006-13. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1091145. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26440216 Free PMC article.
-
Specificity protein 1-modulated superoxide dismutase 2 enhances temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma, which is independent of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase.Redox Biol. 2017 Oct;13:655-664. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28822335 Free PMC article.
-
RECQ1 expression is upregulated in response to DNA damage and in a p53-dependent manner.Oncotarget. 2017 May 27;8(44):75924-75942. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18237. eCollection 2017 Sep 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29100281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christmann M, Tomicic MT, Roos WP, Kaina B. Mechanisms of human DNA repair: an update. Toxicology. 2003;193:3–34. - PubMed
-
- Samson L, Cairns J. A new pathway for DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977;267:281–283. - PubMed
-
- Jeggo P, Defais TM, Samson L, Schendel P. An adaptive response of E. coli to low levels of alkylating agent: comparison with previously characterised DNA repair pathways. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1977;157:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

