PIK3CA and AKT1 mutations have distinct effects on sensitivity to targeted pathway inhibitors in an isogenic luminal breast cancer model system
- PMID: 23888070
- PMCID: PMC3805128
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0884
PIK3CA and AKT1 mutations have distinct effects on sensitivity to targeted pathway inhibitors in an isogenic luminal breast cancer model system
Abstract
Purpose: Activating mutations in the phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mTOR pathway are present in the majority of breast cancers and therefore are a major focus of drug development and clinical trials. Pathway mutations have been proposed as predictive biomarkers for efficacy of PI3K-targeted therapies. However, the precise contribution of distinct PI3K pathway mutations to drug sensitivity is unknown.
Experimental design: We describe the creation of a physiologic human luminal breast cancer cell line model to study the phenotype of these mutations using the MCF-7 cell line. We used somatic cell gene targeting to "correct" PIK3CA E545K-mutant alleles in MCF-7 cells to wild-type sequence. The AKT1 E17K hotspot mutation was knocked in on this wild-type background.
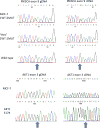
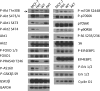
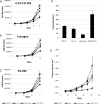
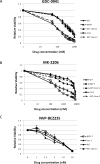
Results: Loss of mutant PIK3CA dramatically reduced phosphorylation of AKT proteins and several known AKT targets, but other AKT target proteins and downstream effectors of mTOR were not affected. PIK3CA wild-type cells exhibited reduced proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Knockin of the AKT1 E17K hotspot mutation on this PIK3CA wild-type background restored pathway signaling, proliferation, and tumor growth in vivo. PIK3CA, but not AKT1 mutation, increased sensitivity to the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 and the allosteric AKT inhibitor MK-2206.
Conclusions: AKT1 E17K is a bona fide oncogene in a human luminal breast cancer context. Distinct PI3K pathway mutations confer differential sensitivity to drugs targeting the pathway at different points and by distinct mechanisms. These findings have implications for the use of tumor genome sequencing to assign patients to targeted therapies.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
BAY 1125976, a selective allosteric AKT1/2 inhibitor, exhibits high efficacy on AKT signaling-dependent tumor growth in mouse models.Int J Cancer. 2017 Jan 15;140(2):449-459. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30457. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27699769
-
The Dual PI3K/mTOR Pathway Inhibitor GDC-0084 Achieves Antitumor Activity in PIK3CA-Mutant Breast Cancer Brain Metastases.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 1;25(11):3374-3383. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3049. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30796030 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insights of Pathways Resulting from Two Common PIK3CA Mutations in Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 1;76(13):3989-4001. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3174. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27197157
-
Mechanism of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: the important role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR in estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2018 Jul;25(4):392-401. doi: 10.1007/s12282-017-0812-x. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29086897 Review.
-
Navigating the complexity of PI3K/AKT pathway in HER-2 negative breast cancer: biomarkers and beyond.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 Aug;200:104404. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104404. Epub 2024 May 28. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38815877 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutant AKT1-E17K is oncogenic in lung epithelial cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 24;6(37):39634-50. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4022. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26053093 Free PMC article.
-
PIK3CA mutation sensitizes breast cancer cells to synergistic therapy of PI3K inhibition and AMPK activation.Invest New Drugs. 2018 Oct;36(5):763-772. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0563-3. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Invest New Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29504069
-
Inhibition of the lncRNA Coded within Transglutaminase 2 Gene Impacts Several Relevant Networks in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Aug 18;7(3):49. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7030049. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 34449674 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of PI3K inhibition in AI-resistant breast cancer cell lines: autophagy, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Nov;190(2):227-240. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06376-4. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34498152
-
Mutations in PIK3CA sensitize breast cancer cells to physiologic levels of aspirin.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Feb;156(1):33-43. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3729-8. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26915040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296:1655–1657. - PubMed
-
- Shaw RJ, Cantley LC. Ras, PI(3)K and mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 2006;441:424–430. - PubMed
-
- Carpten JD, Faber AL, Horn C, Donoho GP, Briggs SL, Robbins CM, et al. A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature. 2007;448:439–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

