A purine scaffold HSP90 inhibitor BIIB021 has selective activity against KSHV-associated primary effusion lymphoma and blocks vFLIP K13-induced NF-κB
- PMID: 23881928
- PMCID: PMC3804723
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3510
A purine scaffold HSP90 inhibitor BIIB021 has selective activity against KSHV-associated primary effusion lymphoma and blocks vFLIP K13-induced NF-κB
Abstract
Purpose: Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV)-associated primary effusion lymphomas (PEL) have extremely poor prognosis when treated with conventional chemotherapy. KSHV-encoded viral FLICE-inhibitory protein (vFLIP) K13 binds to the IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex to constitutively activate the NF-κB pathway, which has been shown to be essential for the survival and proliferation of PEL cells. The molecular chaperone HSP90 is a component of the IKK complex and is required for its activity.
Experimental design: We have analyzed the effect of HSP90 inhibitors on the survival and proliferation of PEL cells and on the activity of the NF-κB pathway.
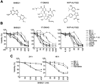
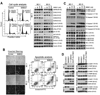
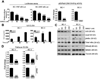
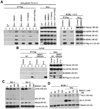
Results: We show that BIIB021, a purine scaffold-based orally administrable HSP90 inhibitor, shows preferential cytotoxicity toward PEL cells as compared with non-PEL cells. The cytotoxic effect of BIIB021 against PEL was associated with induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. BIIB021 blocked the expression of a number of cellular proteins involved in the regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis. BIIB021 also blocked constitutive NF-κB activity present in PEL cells, in part, by blocking the interaction of vFLIP K13 with the IKK complex subunits. In a xenograft model of PEL, BIIB021 significantly reduced tumor growth.
Conclusion: BIIB021 blocks constitutive NF-κB activity in PEL and shows preferential antitumor activity against PEL in vitro and in vivo. BIIB021 may be a promising agent for treatment of PEL.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effects of heat shock protein 90 inhibitors on apoptosis and viral replication in primary effusion lymphoma cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(5):725-30. doi: 10.1248/bpb.35.725. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012. PMID: 22687408
-
Nm23-H1 induces apoptosis in primary effusion lymphoma cells via inhibition of NF-κB signaling through interaction with oncogenic latent protein vFLIP K13 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Oct;45(5):967-989. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00701-9. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 35964258
-
Biscoclaurine alkaloid cepharanthine inhibits the growth of primary effusion lymphoma in vitro and in vivo and induces apoptosis via suppression of the NF-kappaB pathway.Int J Cancer. 2009 Sep 15;125(6):1464-72. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24521. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19521981
-
BIIB021, an Hsp90 inhibitor: A promising therapeutic strategy for blood malignancies (Review).Oncol Rep. 2018 Jul;40(1):3-15. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6422. Epub 2018 May 8. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29749536 Review.
-
Current status of treatment for primary effusion lymphoma.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2014 Aug;3(3):65-74. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2014.01010. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2014. PMID: 25364646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The heat shock protein 90 inhibitor BIIB021 suppresses the growth of T and natural killer cell lymphomas.Front Microbiol. 2015 Apr 9;6:280. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00280. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25914683 Free PMC article.
-
Olanzapine's effects on hypothalamic transcriptomics and kinase activity.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2024 May;163:106987. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2024.106987. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38340539
-
Development and characterization of a novel luciferase based cytotoxicity assay.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 9;8(1):199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18606-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29317736 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of prosurvival pathways as therapeutic approaches against primary effusion lymphomas: past, present, and Future.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:104912. doi: 10.1155/2015/104912. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25695042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of virus-induced NF-κB signaling by NEMO coiled coil mimics.Nat Commun. 2020 Apr 14;11(1):1786. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15576-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32286300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nador RG, Cesarman E, Chadburn A, Dawson DB, Ansari MQ, Sald J, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity associated with the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus. Blood. 1996;88:645–656. - PubMed
-
- Boulanger E, Gerard L, Gabarre J, Molina JM, Rapp C, Abino JF, et al. Prognostic factors and outcome of human herpesvirus 8-associated primary effusion lymphoma in patients with AIDS. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4372–4380. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Keller SA, Schattner EJ, Cesarman E. Inhibition of NF-kappaB induces apoptosis of KSHV-infected primary effusion lymphoma cells. Blood. 2000;96:2537–2542. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Eby MT, Rathore N, Sinha SK, Kumar A, Chaudhary PM. The Human Herpes Virus 8-encoded Viral FLICE Inhibitory Protein Physically Associates with and Persistently Activates the Ikappa B Kinase Complex. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:13745–13751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

