PUMA Cooperates with p21 to Regulate Mammary Epithelial Morphogenesis and Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition
- PMID: 23805223
- PMCID: PMC3689819
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066464
PUMA Cooperates with p21 to Regulate Mammary Epithelial Morphogenesis and Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition
Erratum in
-
Correction: PUMA Cooperates with p21 to Regulate Mammary Epithelial Morphogenesis and Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 7;15(8):e0237624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237624. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32764807 Free PMC article.
Abstract
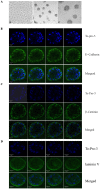
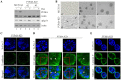
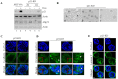
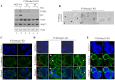
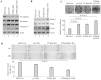
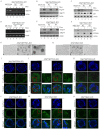
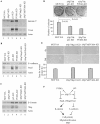
Lumen formation is essential for mammary morphogenesis and requires proliferative suppression and apoptotic clearance of the inner cells within developing acini. Previously, we showed that knockdown of p53 or p73 leads to aberrant mammary acinus formation accompanied with decreased expression of p53 family targets PUMA and p21, suggesting that PUMA, an inducer of apoptosis, and p21, an inducer of cell cycle arrest, directly regulate mammary morphogenesis. To address this, we generated multiple MCF10A cell lines in which PUMA, p21, or both were stably knocked down. We found that morphogenesis of MCF10A cells was altered modestly by knockdown of either PUMA or p21 alone but markedly by knockdown of both PUMA and p21. Moreover, we found that knockdown of PUMA and p21 leads to loss of E-cadherin expression along with increased expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers. Interestingly, we found that knockdown of ΔNp73, which antagonizes the ability of wide-type p53 and TA isoform of p73 to regulate PUMA and p21, mitigates the abnormal morphogenesis and EMT induced by knockdown of PUMA or p21. Together, our data suggest that PUMA cooperates with p21 to regulate normal acinus formation and EMT.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
P73 tumor suppressor and its targets, p21 and PUMA, are required for madin-darby canine kidney cell morphogenesis by maintaining an appropriate level of epithelial to mesenchymal transition.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 10;6(16):13994-4004. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4374. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26101856 Free PMC article.
-
Mammary epithelial cell polarity is regulated differentially by p73 isoforms via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 18;287(21):17746-17753. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.358143. Epub 2012 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22457351 Free PMC article.
-
Combined loss of PUMA and p21 accelerates c-MYC-driven lymphoma development considerably less than loss of one allele of p53.Oncogene. 2016 Jul 21;35(29):3866-71. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.457. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26640149
-
p53-Dependent p21-mediated growth arrest pre-empts and protects HCT116 cells from PUMA-mediated apoptosis induced by EGCG.Cancer Lett. 2010 Oct 28;296(2):225-32. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.04.012. Epub 2010 May 4. Cancer Lett. 2010. PMID: 20444544 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Role of p73 in Cancer Microenvironment and DNA Damage Response.Cells. 2021 Dec 13;10(12):3516. doi: 10.3390/cells10123516. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34944027 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing of p53 and CDKN1A establishes sustainable immortalized megakaryocyte progenitor cells from human iPSCs.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Dec 14;16(12):2861-2870. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.11.001. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 34861163 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of miR-106b in tumorigenic actions of both prolactin and estradiol.Oncotarget. 2017 May 30;8(22):36368-36382. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16755. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28422740 Free PMC article.
-
Differential mechanisms underlying methotrexate-induced cell death and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 cells.Toxicol Res. 2020 Oct 27;37(3):293-300. doi: 10.1007/s43188-020-00067-w. eCollection 2021 Jul. Toxicol Res. 2020. PMID: 34295794 Free PMC article.
-
P73 tumor suppressor and its targets, p21 and PUMA, are required for madin-darby canine kidney cell morphogenesis by maintaining an appropriate level of epithelial to mesenchymal transition.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 10;6(16):13994-4004. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4374. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26101856 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminase 2 contributes to a TP53-induced autophagy program to prevent oncogenic transformation.Elife. 2016 Mar 9;5:e07101. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07101. Elife. 2016. PMID: 26956429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Debnath J, Mills KR, Collins NL, Reginato MJ, Muthuswamy SK, et al. (2002) The role of apoptosis in creating and maintaining luminal space within normal and oncogene-expressing mammary acini. Cell 111: 29–40. - PubMed
-
- Strange R, Metcalfe T, Thackray L, Dang M (2001) Apoptosis in normal and neoplastic mammary gland development. Microsc Res Tech 52: 171–181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

