YKL-40 acts as an angiogenic factor to promote tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 23755018
- PMCID: PMC3664773
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00122
YKL-40 acts as an angiogenic factor to promote tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
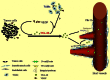
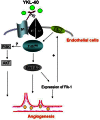
A secreted glycoprotein YKL-40 also named chitinase-3-like-1 is normally expressed by multiple cell types such as macrophages, chondrocytes, and vascular smooth muscle cells. However, a prominently high level of YKL-40 was found in a wide spectrum of human diseases including cancers and chronic inflammatory diseases where it was strongly expressed by cancerous cells and infiltrating macrophages. Here, we summarized recent important findings of YKL-40 derived from cancerous cells and smooth muscle cells during tumor angiogenesis and development. YKL-40 is a potent angiogenic factor capable of stimulating tumor vascularization mediated by endothelial cells and maintaining vascular integrity supported by smooth muscle cells. In addition, YKL-40 induces FAK-MAPK signaling and up-regulates VEGF receptor 2 in endothelial cells; but a neutralizing antibody (mAY) against YKL-40 inhibits its angiogenic activity. While YKL-40 is essential for angiogenesis, little is known about its functional role in tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-mediated tumor development. Therefore, significant efforts are urgently needed to identify pathophysiological function of YKL-40 in the dynamic interaction between tumor cells and TAMs in the tumor microenvironment, which may offer substantial mechanistic insights into tumor angiogenesis and metastasis, and also point to a therapeutic target for treatment of cancers and other diseases.
Keywords: VEGF; YKL-40; angiogenesis; neutralizing anti-YKL-40 antibody; tumor cells; tumor microenvironment; tumor-associated macrophages; vascular endothelial cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of tumor associated macrophages in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.Front Physiol. 2014 Mar 5;5:75. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00075. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24634660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A YKL-40-neutralizing antibody blocks tumor angiogenesis and progression: a potential therapeutic agent in cancers.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 May;10(5):742-51. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0868. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21357475 Free PMC article.
-
Role of YKL-40 in the angiogenesis, radioresistance, and progression of glioblastoma.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 29;286(17):15332-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.212514. Epub 2011 Mar 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21385870 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-derived mural-like cells coordinate with endothelial cells: role of YKL-40 in mural cell-mediated angiogenesis.Oncogene. 2014 Apr 17;33(16):2110-22. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.160. Epub 2013 May 13. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23665676 Free PMC article.
-
YKL-39 as a Potential New Target for Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Cancer.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 22;10:2930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02930. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32038607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor‑associated macrophages activated in the tumor environment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Characterization and treatment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Oct;65(4):100. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5688. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39239752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Targeting via siRNA-COG3 to Suppress Tumor Progression in Mice and Inhibit Cancer Metastasis and Angiogenesis in Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines.Microrna. 2024;13(2):140-154. doi: 10.2174/0122115366275856240101083442. Microrna. 2024. PMID: 38243930
-
YKL-40 in the diagnosis, prediction of prognosis, and platinum sensitivity in serous epithelial ovarian cancer.Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Sep;15(3):177-181. doi: 10.4274/tjod.28459. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 30202628 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoengineering strategies to enhance vascularization and tissue regeneration.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 May;184:114233. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114233. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35304171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated YKL-40 serum levels may contribute to wet age-related macular degeneration via the ERK1/2 pathway.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Nov;11(11):2933-2942. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13223. Epub 2021 Sep 30. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 34110111 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

