MicroRNAs in liver disease
- PMID: 23689081
- PMCID: PMC4091636
- DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.87
MicroRNAs in liver disease
Abstract
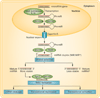
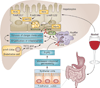
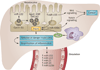
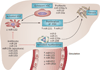
Small, noncoding microRNAs (miRNAs) regulate diverse biological functions in the liver and increasing evidence suggests that they have a role in liver pathology. This Review summarizes advances in the field of miRNAs in liver diseases, inflammation and cirrhosis. MicroRNA-122, the most abundant miRNA in hepatocytes, has well-defined roles in HCV replication, and data indicate that it also serves as a viable therapeutic target. The role of miR-122 is also emerging in other liver diseases. Ample evidence exists for the important regulatory potential of other miRNAs in conditions associated with liver inflammation related to alcohol use, the metabolic syndrome or autoimmune processes. In addition, a broad array of miRNAs have been associated with the development of liver fibrosis both in animal models and human studies. The significance of the function and cellular distribution of miRNAs in the liver and the potential of miRNAs as a means of communication between cells and organs is discussed as well as the emerging utility of circulating miRNAs as biomarkers of different forms of liver damage and as early markers of disease and progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Importantly, miRNA modulation in the liver represents a new therapeutic approach in the treatment armamentarium of hepatologists in the future.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-122 in hepatic function and liver diseases.Protein Cell. 2012 May;3(5):364-71. doi: 10.1007/s13238-012-2036-3. Epub 2012 May 18. Protein Cell. 2012. PMID: 22610888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases.Gut. 2021 Apr;70(4):784-795. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322526. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Gut. 2021. PMID: 33127832 Review.
-
miR-122, a paradigm for the role of microRNAs in the liver.J Hepatol. 2008 Apr;48(4):648-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.01.019. Epub 2008 Feb 12. J Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18291553 Review.
-
The role of miRNAs in liver diseases: Potential therapeutic and clinical applications.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Mar;243:154375. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154375. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 36801506 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in alcoholic liver disease: Recent advances and future applications.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;234(1):382-394. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26938. Epub 2018 Aug 4. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30076710 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-based diagnostic tools for advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B and C.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 12;6:34935. doi: 10.1038/srep34935. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27731343 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cytokine-induced modulation of microRNA expression and secretion as measured by a novel microRNA specific qPCR assay.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 25;5:11590. doi: 10.1038/srep11590. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26108880 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling circulating microRNAs in patients with cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure.JHEP Rep. 2021 Jan 19;3(2):100233. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100233. eCollection 2021 Apr. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 33665588 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker discovery: quantification of microRNAs and other small non-coding RNAs using next generation sequencing.BMC Med Genomics. 2015 Jul 1;8:35. doi: 10.1186/s12920-015-0109-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26130076 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Dicer1 impairs hepatocyte survival and leads to chronic inflammation and progenitor cell activation.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 7;21(21):6591-603. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6591. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26074697 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

