Critical structure sparing in stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for central lung lesions: helical tomotherapy vs. volumetric modulated arc therapy
- PMID: 23577071
- PMCID: PMC3618449
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059729
Critical structure sparing in stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for central lung lesions: helical tomotherapy vs. volumetric modulated arc therapy
Abstract
Background: Helical tomotherapy (HT) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) are both advanced techniques of delivering intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT). Here, we conduct a study to compare HT and partial-arc VMAT in their ability to spare organs at risk (OARs) when stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) is delivered to treat centrally located early stage non-small-cell lung cancer or lung metastases.
Methods: 12 patients with centrally located lung lesions were randomly chosen. HT, 2 & 8 arc (Smart Arc, Pinnacle v9.0) plans were generated to deliver 70 Gy in 10 fractions to the planning target volume (PTV). Target and OAR dose parameters were compared. Each technique's ability to meet dose constraints was further investigated.
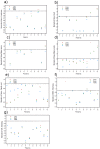
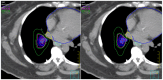
Results: HT and VMAT plans generated essentially equivalent PTV coverage and dose conformality indices, while a trend for improved dose homogeneity by increasing from 2 to 8 arcs was observed with VMAT. Increasing the number of arcs with VMAT also led to some improvement in OAR sparing. After normalizing to OAR dose constraints, HT was found to be superior to 2 or 8-arc VMAT for optimal OAR sparing (meeting all the dose constraints) (p = 0.0004). All dose constraints were met in HT plans. Increasing from 2 to 8 arcs could not help achieve optimal OAR sparing for 4 patients. 2/4 of them had 3 immediately adjacent structures.
Conclusion: HT appears to be superior to VMAT in OAR sparing mainly in cases which require conformal dose avoidance of multiple immediately adjacent OARs. For such cases, increasing the number of arcs in VMAT cannot significantly improve OAR sparing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive dosimetric planning comparison for early-stage, non-small cell lung cancer with SABR: fixed-beam IMRT versus VMAT versus TomoTherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 Sep 8;17(5):329-340. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i5.6291. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27685129 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of helical tomotherapy in stereotactic body radiation therapy for centrally located early stage non‒small-cell lung cancer or lung metastases.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Nov 1;81(3):856-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.11.051. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 21255942
-
Analysis of dose distribution and risk of pneumonitis in stereotactic body radiation therapy for centrally located lung tumors: a comparison of robotic radiosurgery, helical tomotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Feb;14(1):49-60. doi: 10.7785/tcrt.2012.500394. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 24325136
-
Technical recommendations for implementation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy and Helical Tomotherapy Total Body Irradiation.Radiother Oncol. 2024 Aug;197:110366. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110366. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Radiother Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38830537 Review.
-
Hippocampal sparing radiation therapy for brain metastases: treatment techniques and clinical implementation.Chin Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;12(5):56. doi: 10.21037/cco-23-73. Chin Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37964545 Review.
Cited by
-
A treatment-planning comparison of three beam arrangement strategies for stereotactic body radiation therapy for centrally located lung tumors using volumetric-modulated arc therapy.J Radiat Res. 2016 Jun;57(3):273-9. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrv105. Epub 2016 Mar 6. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 26951076 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and efficacy of helical intensity-modulated radiotherapy for stage III non-small cell lung cancer in comparison with conventionally fractionated 3D-CRT.J Thorac Dis. 2016 May;8(5):862-71. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.03.46. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 27162660 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two RapidArc Delivery Strategies in Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy of Peripheral Lung Cancer with Flattening Filter Free Beams.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 1;10(7):e0127501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127501. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26131554 Free PMC article.
-
Hypo-fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for lung malignancies by means of helical tomotherapy: report of feasibility by a single-center experience.Radiol Med. 2018 Jun;123(6):406-414. doi: 10.1007/s11547-018-0858-7. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Radiol Med. 2018. PMID: 29455424
-
Comparison of outcomes of stereotactic body radiation therapy delivered with three different technologies to the lung.J Radiosurg SBRT. 2018;5(3):209-216. J Radiosurg SBRT. 2018. PMID: 29988318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chi A, Liao Z, Nguyen NP, Xu J, Stea B, et al. (2010) Systemic review of the patterns of failure following stereotactic body radiation therapy in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: Clinical implication. Radiother Oncol 94: 1–11. - PubMed
-
- Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, et al. (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81: 1352–1358. - PubMed
-
- Ricardi U, Filippi AR, Guarneri A, Ragona R, Mantovani C, et al. (2012) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung metastases. Lung Cancer 75: 77–81. - PubMed
-
- Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, et al. (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HypoFXSRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: updated results of 257 patients in a Japanese multi-institutional study. J Thorac Oncol 2: S94–100. - PubMed
-
- Oshiro Y, Aruga T, Tsuboi K, Marino K, Hara R, et al. (2010) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumors at the pulmonary hilum. Strahlenther Onkol 186: 274–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

