Lysine acetyltransferase GCN5 potentiates the growth of non-small cell lung cancer via promotion of E2F1, cyclin D1, and cyclin E1 expression
- PMID: 23543735
- PMCID: PMC3656305
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.458737
Lysine acetyltransferase GCN5 potentiates the growth of non-small cell lung cancer via promotion of E2F1, cyclin D1, and cyclin E1 expression
Abstract
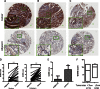
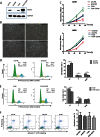
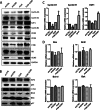
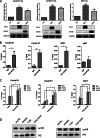
The lysine acetyltransferases play crucial but complex roles in cancer development. GCN5 is a lysine acetyltransferase that generally regulates gene expression, but its role in cancer development remains largely unknown. In this study, we report that GCN5 is highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancer tissues and that its expression correlates with tumor size. We found that the expression of GCN5 promotes cell growth and the G1/S phase transition in multiple lung cancer cell lines. Further study revealed that GCN5 regulates the expression of E2F1, cyclin D1, and cyclin E1. Our reporter assays indicated that the expression of GCN5 enhances the activities of the E2F1, cyclin D1, and cyclin E1 promoters. ChIP experiments suggested that GCN5 binds directly to these promoters and increases the extent of histone acetylation within these regions. Mechanistic studies suggested that GCN5 interacts with E2F1 and is recruited by E2F1 to the E2F1, cyclin D1, and cyclin E1 promoters. The function of GCN5 in lung cancer cells is abrogated by the knockdown of E2F1. Finally, we confirmed that GCN5 regulates the expression of E2F1, cyclin D1, and cyclin E1 and potentiates lung cancer cell growth in a mouse tumor model. Taken together, our results demonstrate that GCN5 specifically potentiates lung cancer growth by directly promoting the expression of E2F1, cyclin D1, and cyclin E1 in an E2F1-dependent manner. Our study identifies a specific and novel function of GCN5 in lung cancer development and suggests that the GCN5-E2F1 interaction represents a potential target for lung cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cancer Prevention; Cancer biology; Cell Cycle; E2F1; GCN5; Gene Regulation; Histone Acetylase; Lung Cancer; Lysine Acetyltransferase (KAT).
Figures
Similar articles
-
The lysine acetyltransferase GCN5 contributes to human papillomavirus oncoprotein E7-induced cell proliferation via up-regulating E2F1.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Nov;22(11):5333-5345. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13806. Epub 2018 Aug 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30079588 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-16-5p enhances radiosensitivity through modulating Cyclin D1/E1-pRb-E2F1 pathway in prostate cancer cells.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):13182-13190. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27989. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30536619
-
miR-218 suppresses gastric cancer cell cycle progression through the CDK6/Cyclin D1/E2F1 axis in a feedback loop.Cancer Lett. 2017 Sep 10;403:175-185. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Jun 17. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28634044
-
The E2F1 transcription factor and RB tumor suppressor moonlight as DNA repair factors.Cell Cycle. 2020 Sep;19(18):2260-2269. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1801190. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 32787501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex functions of Gcn5 and Pcaf in development and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194609. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194609. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32730897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleolar and spindle‑associated protein 1 promotes non‑small cell lung cancer progression and serves as an effector of myocyte enhancer factor 2D.Oncol Rep. 2021 Mar;45(3):1044-1058. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7918. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33650655 Free PMC article.
-
KATs in cancer: functions and therapies.Oncogene. 2015 Sep 17;34(38):4901-13. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.453. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25659580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic aspects of c-MYC signaling in inflammatory and cancerous colonic diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep 21;22(35):7938-50. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i35.7938. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27672289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WDHD1 facilitates G1 checkpoint abrogation in HPV E7 expressing cells by modulating GCN5.BMC Cancer. 2020 Sep 3;20(1):840. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07287-1. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32883234 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Activation of MYC-Induced Genes by GCN5 Promotes B-cell Lymphomagenesis.Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 15;80(24):5543-5553. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2379. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33168647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Icardi L., De Bosscher K., Tavernier J. (2012) The HAT/HDAC interplay: multilevel control of STAT signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 23, 283–291 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad M., Hamid A., Hussain A., Majeed R., Qurishi Y., Bhat J. A., Najar R. A., Qazi A. K., Zargar M. A., Singh S. K., Saxena A. K. (2012) Understanding histone deacetylases in the cancer development and treatment: an epigenetic perspective of cancer chemotherapy. DNA Cell Biol. 31, S62–S71 - PubMed
-
- Ma J., Wang J. D., Zhang W. J., Zou B., Chen W. J., Lam C. S., Chen M. H., Pang R., Tan V. P., Hung I. F., Lan H. Y., Wang Q. Y., Wong B. C. (2010) Promoter hypermethylation and histone hypoacetylation contribute to pancreatic-duodenal homeobox 1 silencing in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis 31, 1552–1560 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

