Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition
- PMID: 23470321
- PMCID: PMC3786574
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3405
Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Jul;13(7):542
Abstract
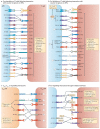
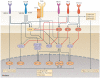
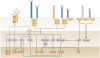
Co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors have a pivotal role in T cell biology, as they determine the functional outcome of T cell receptor (TCR) signalling. The classic definition of T cell co-stimulation continues to evolve through the identification of new co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors, the biochemical characterization of their downstream signalling events and the delineation of their immunological functions. Notably, it has been recently appreciated that co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors display great diversity in expression, structure and function, and that their functions are largely context dependent. Here, we focus on some of these emerging concepts and review the mechanisms through which T cell activation, differentiation and function is controlled by co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of costimulation.Immunol Rev. 2009 May;229(1):5-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00784.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19426211 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
T cell receptor signaling can directly enhance the avidity of CD28 ligand binding.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 24;9(2):e89263. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089263. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586641 Free PMC article.
-
A costimulation-initiated signaling pathway regulates NFATc1 transcription in T lymphocytes.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 15;179(2):1096-103. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.2.1096. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17617602
-
Yin-Yang of costimulation: crucial controls of immune tolerance and function.Immunol Rev. 2009 May;229(1):88-100. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00769.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19426216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accessory Molecule and Costimulation Requirements for CD4 T Cell Response.Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(2-6):261-290. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v37.i2-6.60. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29773023 Review.
Cited by
-
In the absence of its cytosolic domain, the CD28 molecule still contributes to T cell activation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jul;72(14):2739-48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1873-7. Epub 2015 Mar 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25725801 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Distribution and Prognostic Value of New Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in HCC Based on a scRNA-Seq Study With CIBERSORTx.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Sep 17;7:451. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00451. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33043022 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of checkpoint markers in the normoxic and hypoxic microenvironment of glioblastomas.Brain Pathol. 2023 Jan;33(1):e13111. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13111. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Brain Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36093941 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Tumor Cell Immune Escape Mediated by CD24/Siglec-10.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 17;11:1324. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01324. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32765491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constrained Cyclic Peptides as Immunomodulatory Inhibitors of the CD2:CD58 Protein-Protein Interaction.ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Aug 19;11(8):2366-74. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00486. Epub 2016 Jul 1. ACS Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27337048 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
June CH, Ledbetter JA, Gillespie MM, Lindsten T, Thompson CB. T-cell proliferation involving the CD28 pathway is associated with cyclosporine-resistant interleukin 2 gene expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1987;7:4472–4481. This paper identified CD28 as a co-stimulator that could amplify TCR signalling to induce proliferation and IL-2 production.
-
-
-
Bretscher P, Cohn M. A theory of self-nonself discrimination. Science. 1970;169:1042–1049. In this paper Bretscher and Cohn first proposed a model in which two signals would be required for cellular activation of B cells as a mechanism of self–non-self discrimination.
-
-
-
Mueller DL, Jenkins MK, Schwartz RH. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: a costimulatory signalling pathway determines the outcome of T cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1989;7:445–480. This paper showed that TCR signalling in the absence of additional signals was insufficient to activate T cells and rendered T cells unresponsive to subsequent stimulation.
-
-
- Saito T, Yokosuka T, Hashimoto-Tane A. Dynamic regulation of T cell activation and co-stimulation through TCR-microclusters. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:4865–4871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA121974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA97085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA085721/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072592/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007247/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI089704/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA142779/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA142779/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA86721/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA121974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI72592/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

