Synergistic effect of the γ-secretase inhibitor PF-03084014 and docetaxel in breast cancer models
- PMID: 23408105
- PMCID: PMC3659764
- DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0096
Synergistic effect of the γ-secretase inhibitor PF-03084014 and docetaxel in breast cancer models
Abstract
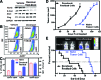
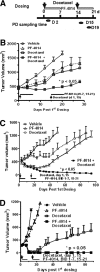
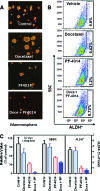
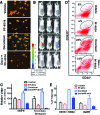
Notch signaling mediates breast cancer cell survival and chemoresistance. In this report, we aimed to evaluate the antitumor efficacy of PF-03084014 in combination with docetaxel in triple-negative breast cancer models. The mechanism of action was investigated. PF-03084014 significantly enhanced the antitumor activity of docetaxel in multiple xenograft models including HCC1599, MDA-MB-231Luc, and AA1077. Docetaxel activated the Notch pathway by increasing the cleaved Notch1 intracellular domain and suppressing the endogenous Notch inhibitor NUMB. PF-03084014 used in combination with docetaxel reversed these effects and demonstrated early-stage synergistic apoptosis. Docetaxel elicited chemoresistance by elevating cytokine release and expression of survivin and induced an endothelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotype by increasing the expressions of Snail, Slug, and N-cadherin. When reimplanted, the docetaxel-residual cells not only became much more tumorigenic, as evidenced by a higher fraction of tumor-initiating cells (TICs), but also showed higher metastatic potential compared with nontreated cells, leading to significantly shortened survival. In contrast, PF-03084014 was able to suppress expression of survivin and MCL1, reduce ABCB1 and ABCC2, upregulate BIM, reverse the EMT phenotype, and diminish the TICs. Additionally, the changes to the ALDH(+) and CD133(+)/CD44(+) subpopulations following therapy corresponded with the TIC self-renewal assay outcome. In summary, PF-03084014 demonstrated synergistic effects with docetaxel through multiple mechanisms. This work provides a strong preclinical rationale for the clinical utility of PF-03084014 to improve taxane therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Notch Pathway Inhibition Using PF-03084014, a γ-Secretase Inhibitor (GSI), Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Docetaxel in Prostate Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 15;21(20):4619-29. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0242. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26202948 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker and pharmacologic evaluation of the γ-secretase inhibitor PF-03084014 in breast cancer models.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Sep 15;18(18):5008-19. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1379. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22806875
-
HepaCAM inhibits the malignant behavior of castration-resistant prostate cancer cells by downregulating Notch signaling and PF-3084014 (a γ-secretase inhibitor) partly reverses the resistance of refractory prostate cancer to docetaxel and enzalutamide in vitro.Int J Oncol. 2018 Jul;53(1):99-112. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4370. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29658567 Free PMC article.
-
Notch Signaling in Breast Cancer: A Role in Drug Resistance.Cells. 2020 Sep 29;9(10):2204. doi: 10.3390/cells9102204. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33003540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Notch signaling pathway as a mediator of tumor survival.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Jul;34(7):1420-30. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt127. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23585460 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mammary gland stem cells and their application in breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):10675-10691. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12893. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27793013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular determinants of all-trans retinoic acid sensitivity in breast cancer: Luminal phenotype and RARα expression.EMBO Mol Med. 2015 Jul;7(7):950-72. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201404670. EMBO Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25888236 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Molecular Classifications of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving Patient Selection for Treatment.Cancer Discov. 2019 Feb;9(2):176-198. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1177. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 30679171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Programs and Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes: Mediators of Breast Cancer Therapy Resistance.Mol Cancer Res. 2020 Sep;18(9):1257-1270. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0067. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Mol Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32503922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NUMB inhibition of NOTCH signalling as a therapeutic target in prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2014 Sep;11(9):499-507. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2014.195. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Nat Rev Urol. 2014. PMID: 25134838 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ranganathan P, Weaver KL, Capobianco AJ. Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:338–351. - PubMed
-
- Cheng L, Alexander R, Zhang S, et al. The clinical and therapeutic implications of cancer stem cell biology. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011;11:1131–1143. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Li D, Liu H, et al. Notch-1 signaling facilitates survivin expression in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11:14–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

