Kruppel-like factor 5 controls villus formation and initiation of cytodifferentiation in the embryonic intestinal epithelium
- PMID: 23266329
- PMCID: PMC3582784
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.12.010
Kruppel-like factor 5 controls villus formation and initiation of cytodifferentiation in the embryonic intestinal epithelium
Abstract
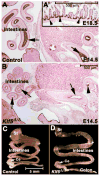
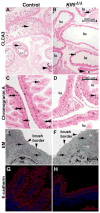
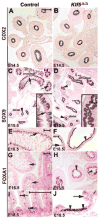
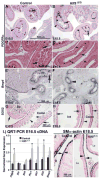
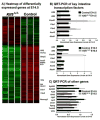
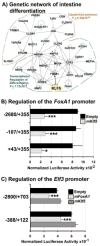
Kruppel-like factor 5 (Klf5) is a transcription factor expressed by embryonic endodermal progenitors that form the lining of the gastrointestinal tract. A Klf5 floxed allele was efficiently deleted from the intestinal epithelium by a Cre transgene under control of the Shh promoter resulting in the inhibition of villus morphogenesis and epithelial differentiation. Although proliferation of the intestinal epithelium was maintained, the expression of Elf3, Pparγ, Atoh1, Ascl2, Neurog3, Hnf4α, Cdx1, and other genes associated with epithelial cell differentiation was inhibited in the Klf5-deficient intestines. At E18.5, Klf5(Δ/Δ) fetuses lacked the apical brush border characteristic of enterocytes, and a loss of goblet and enteroendocrine cells was observed. The failure to form villi was not attributable to the absence of HH or PDGF signaling, known mediators of this developmental process. Klf5-deletion blocked the decrease in FoxA1 and Sox9 expression that accompanies normal villus morphogenesis. KLF5 directly inhibited activity of the FoxA1 promoter, and in turn FOXA1 inhibited Elf3 gene expression in vitro, linking the observed loss of Elf3 with the persistent expression of FoxA1 observed in Klf5-deficient mice. Genetic network analysis identified KLF5 as a key transcription factor regulating intestinal cell differentiation and cell adhesion. These studies indicate a novel requirement for KLF5 to initiate morphogenesis of the early endoderm into a compartmentalized intestinal epithelium comprised of villi and terminally differentiated cells.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Krüppel-like factor 5 is important for maintenance of crypt architecture and barrier function in mouse intestine.Gastroenterology. 2011 Oct;141(4):1302-13, 1313.e1-6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.086. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21763241 Free PMC article.
-
Krüpple-like factor 5 is required for proper maintenance of adult intestinal crypt cellular proliferation.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Jan;60(1):86-100. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3307-z. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25069574 Free PMC article.
-
Kruppel-like factor 5 is required for formation and differentiation of the bladder urothelium.Dev Biol. 2011 Oct 1;358(1):79-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.020. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21803035 Free PMC article.
-
The diverse functions of Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5 in epithelial biology and pathobiology.Bioessays. 2007 Jun;29(6):549-57. doi: 10.1002/bies.20581. Bioessays. 2007. PMID: 17508399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Krüppel-like factor 5 in kidney disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Mar;25(5):2342-2355. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16332. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33523554 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissection of transcriptional and cis-regulatory control of differentiation in human pancreatic cancer.EMBO J. 2016 Mar 15;35(6):595-617. doi: 10.15252/embj.201592404. Epub 2016 Jan 14. EMBO J. 2016. PMID: 26769127 Free PMC article.
-
Stem Cell Lineage Infidelity Drives Wound Repair and Cancer.Cell. 2017 May 4;169(4):636-650.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.042. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28434617 Free PMC article.
-
Different expression patterns and functions of acetylated and unacetylated Klf5 in the proliferation and differentiation of prostatic epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 5;8(6):e65538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065538. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23755247 Free PMC article.
-
Goblet cells of the conjunctiva: A review of recent findings.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016 Sep;54:49-63. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 27091323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Balance between Differentiation and Terminal Differentiation Maintains Oral Epithelial Homeostasis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 13;13(20):5123. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205123. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680271 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aizawa K, Suzuki T, Kada N, Ishihara A, Kawai-Kowase K, Matsumura T, Sasaki K, Munemasa Y, Manabe I, Kurabayashi M, Collins T, Nagai R. Regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-A chain by Kruppel-like factor 5: new pathway of cooperative activation with nuclear factor-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:70–76. - PubMed
-
- Bagheri-Fam S, Barrionuevo F, Dohrmann U, Gunther T, Schule R, Kemler R, Mallo M, Kanzler B, Scherer G. Long-range upstream and downstream enhancers control distinct subsets of the complex spatiotemporal Sox9 expression pattern. Dev Biol. 2006;291:382–397. - PubMed
-
- Bateman NW, Tan D, Pestell RG, Black JD, Black AR. Intestinal tumor progression is associated with altered function of KLF5. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:12093–12101. - PubMed
-
- Besnard V, Wert SE, Hull WM, Whitsett JA. Immunohistochemical localization of Foxa1 and Foxa2 in mouse embryos and adult tissues. Gene Expr Patterns. 2004;5:193–208. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

