Marqibo® (vincristine sulfate liposome injection) improves the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vincristine
- PMID: 23212117
- PMCID: PMC3579462
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-012-2042-4
Marqibo® (vincristine sulfate liposome injection) improves the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vincristine
Abstract
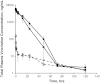
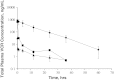
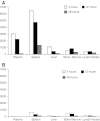
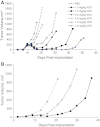
Vincristine (VCR) is a mainstay of treatment of hematologic malignancies and solid tumors due to its well-defined mechanism of action, demonstrated anticancer activity and its ability to be combined with other agents. VCR is an M-phase cell cycle-specific anticancer drug with activity that is concentration and exposure duration dependent. The pharmacokinetic profile of standard VCR is described by a bi-exponential elimination pattern with a very fast initial distribution half-life followed by a longer elimination half-life. VCR also has a large volume of distribution, suggesting diffuse distribution and tissue binding. These properties may limit optimal drug exposure and delivery to target tissues as well as clinical utility as a single agent or as an effective component of multi-agent regimens. Vincristine sulfate liposome injection (VSLI), Marqibo(®), is a sphingomyelin and cholesterol-based nanoparticle formulation of VCR that was designed to overcome the dosing and pharmacokinetic limitations of standard VCR. VSLI was developed to increase the circulation time, optimize delivery to target tissues and facilitate dose intensification without increasing toxicity. In xenograft studies in mice, VSLI had a higher maximum tolerated dose, superior antitumor activity and delivered higher amounts of active drug to target tissues compared to standard VCR. VSLI recently received accelerated FDA approval for use in adults with advanced, relapsed and refractory Philadelphia chromosome-negative ALL and is in development for untreated adult ALL, pediatric ALL and untreated aggressive NHL. Here, we summarize the nonclinical data for VSLI that support its continued clinical development and recent approval for use in adult ALL.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vincristine sulfate liposome injection (VSLI) in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;53(11):1139-45. doi: 10.1002/jcph.155. Epub 2013 Aug 17. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23907766 Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of vincristine and vincristine sulfate liposomes injection (VSLI, marqibo®) after intravenous administration in Non-human primates.Invest New Drugs. 2016 Feb;34(1):61-5. doi: 10.1007/s10637-015-0311-x. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Invest New Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26661090 Free PMC article.
-
High-dose vincristine sulfate liposome injection for advanced, relapsed, and refractory adult Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Feb 20;31(6):676-83. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.2309. Epub 2012 Nov 19. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23169518 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Vincristine Sulfate Liposome Injection in the Treatment of Adult Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia.Oncologist. 2016 Jul;21(7):840-7. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0391. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27328933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vincristine sulfate liposome injection: a guide to its use in refractory or relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia.BioDrugs. 2013 Feb;27(1):69-74. doi: 10.1007/s40259-012-0002-5. BioDrugs. 2013. PMID: 23329395 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein nanoparticles in drug delivery: animal protein, plant proteins and protein cages, albumin nanoparticles.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 May 29;19(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00896-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34051806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicines for renal disease: current status and future applications.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Dec;12(12):738-753. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.156. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27795549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric nanoparticles loaded with vincristine and carbon dots for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy and imaging.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 18;14(1):24520. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75332-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39424827 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to anti-tubulin agents: From vinca alkaloids to epothilones.Cancer Drug Resist. 2019 Mar 19;2(1):82-106. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2019.06. eCollection 2019. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 35582143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vincristine sulfate liposomal injection for acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:4361-9. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S54657. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 24232122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Johnson IS, Armstrong JG, Gorman M, Burnett JP., Jr The vinca alkaloids: a new class of oncolytic agents. Cancer Res. 1963;23:1390–1427. - PubMed
-
- van Tellingen O, Sips JH, Beijnen JH, Bult A, Nooijen WJ. Pharmacology, bio-analysis and pharmacokinetics of the vinca alkaloids and semi-synthetic derivatives (review) Anticancer Res. 1992;12(5):1699–1715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

