A laboratory-developed TaqMan Array Card for simultaneous detection of 19 enteropathogens
- PMID: 23175269
- PMCID: PMC3553916
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02658-12
A laboratory-developed TaqMan Array Card for simultaneous detection of 19 enteropathogens
Abstract
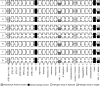
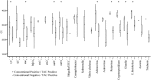
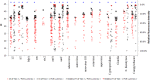
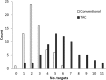
The TaqMan Array Card (TAC) system is a 384-well singleplex real-time PCR format that has been used to detect multiple infection targets. Here we developed an enteric TaqMan Array Card to detect 19 enteropathogens, including viruses (adenovirus, astrovirus, norovirus GII, rotavirus, and sapovirus), bacteria (Campylobacter jejuni/C. coli, Clostridium difficile, Salmonella, Vibrio cholerae, diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains including enteroaggregative E. coli [EAEC], enterotoxigenic E. coli [ETEC], enteropathogenic E. coli [EPEC], and Shiga-toxigenic E. coli [STEC]), Shigella/enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC), protozoa (Cryptosporidium, Giardia lamblia, and Entamoeba histolytica), and helminths (Ascaris lumbricoides and Trichuris trichiura), as well as two extrinsic controls to monitor extraction and amplification efficiency (the bacteriophage MS2 and phocine herpesvirus). Primers and probes were newly designed or adapted from published sources and spotted onto microfluidic cards. Fecal samples were spiked with extrinsic controls, and DNA and RNA were extracted using the QiaAmp Stool DNA minikit and the QuickGene RNA Tissue kit, respectively, and then mixed with Ag-Path-ID One Step real-time reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) reagents and loaded into cards. PCR efficiencies were between 90% and 105%, with linearities of 0.988 to 1. The limit of detection of the assays in the TAC was within a 10-fold difference from the cognate assays performed on plates. Precision testing demonstrated a coefficient of variation of below 5% within a run and 14% between runs. Accuracy was evaluated for 109 selected clinical specimens and revealed an average sensitivity and specificity of 85% and 77%, respectively, compared with conventional methods (including microscopy, culture, and immunoassay) and 98% and 96%, respectively, compared with our laboratory-developed PCR-Luminex assays. This TAC allows fast, accurate, and quantitative detection of a broad spectrum of enteropathogens and is well suited for surveillance or clinical purposes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Luminex xTAG gastrointestinal pathogen analyte-specific reagents for high-throughput, simultaneous detection of bacteria, viruses, and parasites of clinical and public health importance.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Sep;51(9):3018-24. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00896-13. Epub 2013 Jul 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23850948 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for rapid detection of 9 pathogens directly from stools of travelers with diarrhea.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Oct;11(10):1300-1307.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.03.037. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23639597
-
The incidence of laboratory-confirmed cases of enteric pathogens in Denmark 2018: a national observational study.Infect Dis (Lond). 2023 May;55(5):340-350. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2023.2183253. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Infect Dis (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36868794
-
Evaluation of multiplex PCRs for diagnosis of infection with diarrheagenic Escherichia coli and Shigella spp.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Dec;42(12):5849-53. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.12.5849-5853.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15583323 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccines for viral and bacterial pathogens causing acute gastroenteritis: Part II: Vaccines for Shigella, Salmonella, enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) enterohemorragic E. coli (EHEC) and Campylobacter jejuni.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(3):601-19. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1011578. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25715096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The epidemiology and impact of persistent Campylobacter infections on childhood growth among children 0-24 months of age in resource-limited settings.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Sep 28;76:102841. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102841. eCollection 2024 Oct. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39380966 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing non-standard nucleic acids for highly sensitive icosaplex (20-plex) detection of microbial threats.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 10:2024.09.09.24313328. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.09.24313328. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39314929 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Epidemiology of Pediatric Astrovirus Gastroenteritis in a Nicaraguan Birth Cohort.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 16;11(9):ofae465. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae465. eCollection 2024 Sep. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39247803 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the dynamics and impact of the gut microbiome on maternal nutritional status during pregnancy, effect on pregnancy outcomes and infant health in rural Pakistan: study protocol for a prospective, longitudinal observational study.BMJ Open. 2024 Aug 12;14(8):e081629. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081629. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39134435 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological Insights into Foodborne Pathogens Through qPCR Exploration of Prevalence - Beijing Municipality, China, January 2022-April 2023.China CDC Wkly. 2024 May 3;6(18):385-389. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2024.075. China CDC Wkly. 2024. PMID: 38737481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kodani M, Yang G, Conklin LM, Travis TC, Whitney CG, Anderson LJ, Schrag SJ, Taylor TH, Jr, Beall BW, Breiman RF, Feikin DR, Njenga MK, Mayer LW, Oberste MS, Tondella ML, Winchell JM, Lindstrom SL, Erdman DD, Fields BS. 2011. Application of TaqMan low-density arrays for simultaneous detection of multiple respiratory pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49:2175–2182 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rachwal PA, Rose HL, Cox V, Lukaszewski RA, Murch AL, Weller SA. 2012. The potential of TaqMan Array Cards for detection of multiple biological agents by real-time PCR. PLoS One 7:e35971 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035971 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

