Contributions of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) to cell immortalization and survival
- PMID: 23170171
- PMCID: PMC3499818
- DOI: 10.3390/v4091537
Contributions of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) to cell immortalization and survival
Abstract
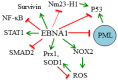
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) immortalizes host cells as part of its latent mode of infection. As a result of this ability to promote cell proliferation and survival, EBV infection contributes to the development of several kinds of B-cell lymphomas and epithelial tumours. The EBV Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) protein is the only EBV protein expressed in all EBV-associated tumours and plays multiple important roles in EBV latency. In addition to its well-studied roles in viral DNA replication, segregation and transcriptional activation, several studies have identified roles of EBNA1 in manipulating cellular processes that result in reduced apoptosis and increased cell survival. This review discusses these cellular effects of EBNA1 and mechanisms by which they occur.
Keywords: EBNA1; NFκB; Nm23-H1; PML; ROS; STAT1; USP7; oxidative stress; p53; survivin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 interacts with Nm23-H1 in lymphoblastoid cell lines and inhibits its ability to suppress cell migration.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1559-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1559-1568.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650182 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 upregulates the cellular antioxidant defense to enable B-cell growth transformation and immortalization.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(3):603-616. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1003-3. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31511648 Free PMC article.
-
Carcinoma-risk variant of EBNA1 deregulates Epstein-Barr Virus episomal latency.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7248-7264. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14540. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28077791 Free PMC article.
-
EBNA1.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:3-34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428370 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 and ZEBRA: targets for therapeutic strategies against EBV-carrying cancers.J Pathol. 2015 Jan;235(2):334-41. doi: 10.1002/path.4431. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25186125 Review.
Cited by
-
EBNA1 inhibitors have potent and selective antitumor activity in xenograft models of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2021 Sep;24(5):1076-1088. doi: 10.1007/s10120-021-01193-6. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Gastric Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33929613 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus-based vaccines against rhesus lymphocryptovirus EBNA-1 induce expansion of specific CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in persistently infected rhesus macaques.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):4721-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03744-13. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24522914 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling the structure of full-length Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1.Virus Genes. 2014 Dec;49(3):358-72. doi: 10.1007/s11262-014-1101-9. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Virus Genes. 2014. PMID: 25011696
-
DNA Oncogenic Virus-Induced Oxidative Stress, Genomic Damage, and Aberrant Epigenetic Alterations.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3179421. doi: 10.1155/2017/3179421. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28740569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GB and gH/gL fusion machinery: a promising target for vaccines to prevent Epstein-Barr virus infection.Arch Virol. 2024 Jul 17;169(8):167. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06095-3. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 39020055 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

