ATM polymorphisms predict severe radiation pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiation therapy
- PMID: 23154078
- PMCID: PMC3594431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.09.024
ATM polymorphisms predict severe radiation pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiation therapy
Abstract
Purpose: The ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) gene mediates detection and repair of DNA damage. We investigated associations between ATM polymorphisms and severe radiation-induced pneumonitis (RP).
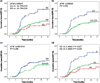
Methods and materials: We genotyped 3 potentially functional single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of ATM (rs1801516 [D1853N/5557G>A], rs189037 [-111G>A] and rs228590) in 362 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), who received definitive (chemo)radiation therapy. The cumulative severe RP probabilities by genotypes were evaluated using the Kaplan-Meier analysis. The associations between severe RP risk and genotypes were assessed by both logistic regression analysis and Cox proportional hazard model with time to event considered.
Results: Of 362 patients (72.4% of non-Hispanic whites), 56 (15.5%) experienced grade ≥3 RP. Patients carrying ATM rs189037 AG/GG or rs228590 TT/CT genotypes or rs189037G/rs228590T/rs1801516G (G-T-G) haplotype had a lower risk of severe RP (rs189037: GG/AG vs AA, adjusted hazard ratio [HR] = 0.49, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.29-0.83, P=.009; rs228590: TT/CT vs CC, HR=0.57, 95% CI, 0.33-0.97, P=.036; haplotype: G-T-G vs A-C-G, HR=0.52, 95% CI, 0.35-0.79, P=.002). Such positive findings remained in non-Hispanic whites.
Conclusions: ATM polymorphisms may serve as biomarkers for susceptibility to severe RP in non-Hispanic whites. Large prospective studies are required to confirm our findings.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATM polymorphisms are associated with risk of radiation-induced pneumonitis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010 Aug 1;77(5):1360-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1675. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010. PMID: 20171797
-
Genetic variants of the LIN28B gene predict severe radiation pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiation therapy.Eur J Cancer. 2014 Jul;50(10):1706-1716. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.03.008. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24780874 Free PMC article.
-
Functional polymorphisms of base excision repair genes XRCC1 and APEX1 predict risk of radiation pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Nov 1;81(3):e67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.11.079. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 21420246 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism rs1801516 in Ataxia Telangiectasia-Mutated Gene Predicts Late Fibrosis in Cancer Patients After Radiotherapy: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(14):e3267. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003267. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27057881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSPB1 polymorphisms might be associated with radiation-induced damage risk in lung cancer patients treated with radiotherapy.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):5743-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4959-4. Epub 2016 Feb 13. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26874728 Review.
Cited by
-
Germline genetic biomarkers to stratify patients for personalized radiation treatment.J Transl Med. 2022 Aug 12;20(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03561-x. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35962345 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-based biomarkers for precision medicine in lung cancer: precision radiation therapy.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017 Dec;6(6):661-669. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.09.12. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29218269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Functional Variants in DNA Repair Genes Are Associated with Efficacy and Toxicity of Radiotherapy in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Oncol. 2020 Jun 24;2020:3132786. doi: 10.1155/2020/3132786. eCollection 2020. J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32684929 Free PMC article.
-
ATM in breast and brain tumors: a comprehensive review.Cancer Biol Med. 2018 Aug;15(3):210-227. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2018.0022. Cancer Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 30197789 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Profiling Reveals Novel Predictive Biomarkers for Chemo-Radiotherapy Efficacy and Thoracic Toxicity in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 14;12:928605. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.928605. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35912186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Perez CA, Pajak TF, Rubin P, et al. Long-term observations of the patterns of failure in patients with unresectable non-oat cell carcinoma of the lung treated with definitive radiotherapy. Report by the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Cancer. 1987;59:1874–1881. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

