Poly-small ubiquitin-like modifier (PolySUMO)-binding proteins identified through a string search
- PMID: 23086935
- PMCID: PMC3516753
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410985
Poly-small ubiquitin-like modifier (PolySUMO)-binding proteins identified through a string search
Abstract
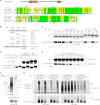
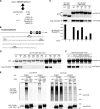
Polysumoylation is a crucial cellular response to stresses against genomic integrity or proteostasis. Like the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO)-targeted ubiquitin ligase RNF4, proteins with clustered SUMO-interacting motifs (SIMs) can be important signal transducers downstream of polysumoylation. To identify novel polySUMO-binding proteins, we conducted a computational string search with a custom Python script. We found clustered SIMs in another RING domain protein Arkadia/RNF111. Detailed biochemical analysis of the Arkadia SIMs revealed that dominant SIMs in a SIM cluster often contain a pentameric VIDLT ((V/I/L/F/Y)(V/I)DLT) core sequence that is also found in the SIMs in PIAS family E3s and is likely the best-fitted structure for SUMO recognition. This idea led to the identification of additional novel SIM clusters in FLASH/CASP8AP2, C5orf25, and SOBP/JXC1. We suggest that the clustered SIMs in these proteins form distinct SUMO binding domains to recognize diverse forms of protein sumoylation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RNF111/Arkadia is a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase that facilitates the DNA damage response.J Cell Biol. 2013 Jun 10;201(6):797-807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201212075. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23751493 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Arkadia/RNF111 structures coordinate its Polycomb body association and transcriptional control.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Aug;34(16):2981-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00036-14. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24912682 Free PMC article.
-
Arkadia, a novel SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase involved in PML degradation.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;33(11):2163-77. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01019-12. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23530056 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1843(1):75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.08.022. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24018209 Review.
-
Control of nuclear activities by substrate-selective and protein-group SUMOylation.Annu Rev Genet. 2013;47:167-86. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-111212-133453. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Annu Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 24016193 Review.
Cited by
-
SUMO and the DNA damage response.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Apr 24;52(2):773-792. doi: 10.1042/BST20230862. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38629643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preserving genome integrity: The vital role of SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases.Cell Insight. 2023 Oct 23;2(6):100128. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2023.100128. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cell Insight. 2023. PMID: 38047137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A CK2 and SUMO-dependent, PML NB-involved regulatory mechanism controlling BLM ubiquitination and G-quadruplex resolution.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 30;14(1):6111. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41705-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37777511 Free PMC article.
-
The Nse5/6-like SIMC1-SLF2 complex localizes SMC5/6 to viral replication centers.Elife. 2022 Nov 14;11:e79676. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79676. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36373674 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Implications of Phase Separation in Cancer.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Nov;9(31):e2202855. doi: 10.1002/advs.202202855. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 36117111 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Creton S., Jentsch S. (2010) SnapShot. The SUMO system. Cell 143, 848–848 - PubMed
-
- Meulmeester E., Melchior F. (2008) Cell biology. SUMO. Nature 452, 709–711 - PubMed
-
- Matunis M. J., Zhang X. D., Ellis N. A. (2006) SUMO. The glue that binds. Dev. Cell 11, 596–597 - PubMed
-
- Minty A., Dumont X., Kaghad M., Caput D. (2000) Covalent modification of p73α by SUMO-1. Two-hybrid screening with p73 identifies novel SUMO-1-interacting proteins and a SUMO-1 interaction motif. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 36316–36323 - PubMed
-
- Hecker C. M., Rabiller M., Haglund K., Bayer P., Dikic I. (2006) Specification of SUMO1- and SUMO2-interacting motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 16117–16127 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

