LoFreq: a sequence-quality aware, ultra-sensitive variant caller for uncovering cell-population heterogeneity from high-throughput sequencing datasets
- PMID: 23066108
- PMCID: PMC3526318
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks918
LoFreq: a sequence-quality aware, ultra-sensitive variant caller for uncovering cell-population heterogeneity from high-throughput sequencing datasets
Abstract
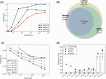
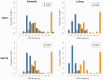
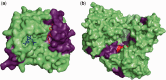
The study of cell-population heterogeneity in a range of biological systems, from viruses to bacterial isolates to tumor samples, has been transformed by recent advances in sequencing throughput. While the high-coverage afforded can be used, in principle, to identify very rare variants in a population, existing ad hoc approaches frequently fail to distinguish true variants from sequencing errors. We report a method (LoFreq) that models sequencing run-specific error rates to accurately call variants occurring in <0.05% of a population. Using simulated and real datasets (viral, bacterial and human), we show that LoFreq has near-perfect specificity, with significantly improved sensitivity compared with existing methods and can efficiently analyze deep Illumina sequencing datasets without resorting to approximations or heuristics. We also present experimental validation for LoFreq on two different platforms (Fluidigm and Sequenom) and its application to call rare somatic variants from exome sequencing datasets for gastric cancer. Source code and executables for LoFreq are freely available at http://sourceforge.net/projects/lofreq/.
Figures

Similar articles
-
QQ-SNV: single nucleotide variant detection at low frequency by comparing the quality quantiles.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Nov 10;16:379. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0812-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26554718 Free PMC article.
-
ViVaMBC: estimating viral sequence variation in complex populations from illumina deep-sequencing data using model-based clustering.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Feb 22;16:59. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0458-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25887734 Free PMC article.
-
Measurements of Intrahost Viral Diversity Are Extremely Sensitive to Systematic Errors in Variant Calling.J Virol. 2016 Jul 11;90(15):6884-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00667-16. Print 2016 Aug 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27194763 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-deep sequencing for the analysis of viral populations.Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Nov;1(5):413-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Curr Opin Virol. 2011. PMID: 22440844 Review.
-
The role of replicates for error mitigation in next-generation sequencing.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Jan;15(1):56-62. doi: 10.1038/nrg3655. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 24322726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Limited cross-species transmission and absence of mutations associated with SARS-CoV-2 adaptation in cats: A case study of infection in a small household setting.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022 May;69(3):1606-1616. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14132. Epub 2021 May 16. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022. PMID: 33908152 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Nanopore and Synthesis-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Platforms for SARS-CoV-2 Variant Monitoring in Wastewater.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 6;24(24):17184. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417184. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139015 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Next-Generation Sequencing to Reveal How Evolutionary Dynamics of Viral Population Shape Dengue Epidemiology.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 19;11:1371. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01371. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32636827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the Genetic Determinants of Telangiectasia and Solid Organ Arteriovenous Malformation Formation in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 12;25(14):7682. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147682. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062925 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid genotyping of targeted viral samples using Illumina short-read sequencing data.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 16;17(9):e0274414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274414. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36112576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eigen M. Selforganization of matter and the evolution of biological macromolecules. Die Naturwissenschaften. 1971;58:465–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

