CXCR1/2 inhibition enhances pancreatic islet survival after transplantation
- PMID: 22996693
- PMCID: PMC3461913
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI63089
CXCR1/2 inhibition enhances pancreatic islet survival after transplantation
Abstract
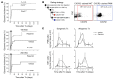
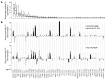
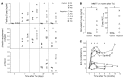
Although long considered a promising treatment option for type 1 diabetes, pancreatic islet cell transformation has been hindered by immune system rejection of engrafted tissue. The identification of pathways that regulate post-transplant detrimental inflammatory events would improve management and outcome of transplanted patients. Here, we found that CXCR1/2 chemokine receptors and their ligands are crucial negative determinants for islet survival after transplantation. Pancreatic islets released abundant CXCR1/2 ligands (CXCL1 and CXCL8). Accordingly, intrahepatic CXCL1 and circulating CXCL1 and CXCL8 were strongly induced shortly after islet infusion. Genetic and pharmacological blockade of the CXCL1-CXCR1/2 axis in mice improved intrahepatic islet engraftment and reduced intrahepatic recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and NKT cells after islet infusion. In humans, the CXCR1/2 allosteric inhibitor reparixin improved outcome in a phase 2 randomized, open-label pilot study with a single infusion of allogeneic islets. These findings indicate that the CXCR1/2-mediated pathway is a regulator of islet damage and should be a target for intervention to improve the efficacy of transplantation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Strategies in Intrahepatic Islet Transplantation: A Comparative Study in Preclinical Models.Transplantation. 2018 Feb;102(2):240-248. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001925. Transplantation. 2018. PMID: 28902069
-
Reparixin, a CXCR1/2 inhibitor in islet allotransplantation.Islets. 2016 Sep 2;8(5):115-24. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2016.1199303. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Islets. 2016. PMID: 27328412 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1-Mediated Early Loss of Transplanted Islets Is Prevented by Anti-IL-6R Antibody in Mice.Pancreas. 2015 Jan;44(1):166-71. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000188. Pancreas. 2015. PMID: 25058889
-
The CXCR1/2 Pathway: Involvement in Diabetes Pathophysiology and Potential Target for T1D Interventions.Curr Diab Rep. 2015 Oct;15(10):68. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0638-x. Curr Diab Rep. 2015. PMID: 26275440 Review.
-
Cell Surface Engineering for Regulation of Immune Reactions in Cell Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;865:189-209. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-18603-0_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26306451 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Islet Transplantation in Humans: Recent Progress and Future Directions.Endocr Rev. 2019 Apr 1;40(2):631-668. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00154. Endocr Rev. 2019. PMID: 30541144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can We Re-Engineer the Endocrine Pancreas?Curr Diab Rep. 2018 Oct 2;18(11):122. doi: 10.1007/s11892-018-1072-7. Curr Diab Rep. 2018. PMID: 30280279 Review.
-
Engineered Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective Review.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 25;10(12):3042. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123042. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rationale and Means to Target Pro-Inflammatory Interleukin-8 (CXCL8) Signaling in Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2013 Aug 6;6(8):929-59. doi: 10.3390/ph6080929. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24276377 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory response in islet transplantation.Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:451035. doi: 10.1155/2014/451035. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Int J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24883060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

