Wild-type EGFR is stabilized by direct interaction with HSP90 in cancer cells and tumors
- PMID: 22952420
- PMCID: PMC3431175
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.12986
Wild-type EGFR is stabilized by direct interaction with HSP90 in cancer cells and tumors
Abstract
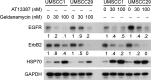
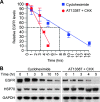
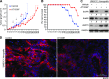
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has been targeted for inhibition using tyrosine kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies, with improvement in outcome in subsets of patients with head and neck, lung, and colorectal carcinomas. We have previously found that EGFR stability plays a key role in cell survival after chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) is known to stabilize mutant EGFR and ErbB2, but its role in cancers with wild-type (WT) WT-EGFR is unclear. In this report, we demonstrate that fully mature, membrane-bound WT-EGFR interacts with HSP90 independent of ErbB2. Further, the HSP90 inhibitors geldanamycin (GA) and AT13387 cause a decrease in WT-EGFR in cultured head and neck cancer cells. This decrease results from a significantly reduced half-life of WT-EGFR. WT-EGFR was also lost in head and neck xenograft specimens after treatment with AT13387 under conditions that inhibited tumor growth and prolonged survival of the mice. Our findings demonstrate that WT-EGFR is a client protein of HSP90 and that their interaction is critical for maintaining both the stability of the receptor as well as the growth of EGFR-dependent cancers. Furthermore, these findings support the search for specific agents that disrupt HSP90's ability to act as an EGFR chaperone.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pnck induces ligand-independent EGFR degradation by probable perturbation of the Hsp90 chaperone complex.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):C1139-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00167.2010. Epub 2011 Feb 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21325639 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of HSP90 Radiosensitizes Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Xenograft by Inhibition of DNA Damage Repair, Nucleotide Metabolism, and Radiation-Induced Tumor Vasculogenesis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Aug 1;110(5):1295-1305. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.03.048. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33838214 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of heat shock protein 90 impairs epidermal growth factor-mediated signaling in gastric cancer cells and reduces tumor growth and vascularization in vivo.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):1123-32. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0628. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17363505
-
Heat shock protein 90 inhibition in lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2008 Jun;3(6 Suppl 2):S152-9. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318174ea3a. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18520302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer.Curr Opin Oncol. 2014 Mar;26(2):159-64. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000047. Curr Opin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24463348 Review.
Cited by
-
HSP90 Inhibitors, Geldanamycin and Radicicol, Enhance Fisetin-Induced Cytotoxicity via Induction of Apoptosis in Human Colonic Cancer Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:987612. doi: 10.1155/2013/987612. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23840275 Free PMC article.
-
A gain-of-function mutant p53-HSF1 feed forward circuit governs adaptation of cancer cells to proteotoxic stress.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Apr 24;5(4):e1194. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.158. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24763051 Free PMC article.
-
The small-molecule kinase inhibitor D11 counteracts 17-AAG-mediated up-regulation of HSP70 in brain cancer cells.PLoS One. 2017 May 18;12(5):e0177706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177706. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542269 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical approaches to targeting hypoxic tumors.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 15;12(12):5351-5374. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36628275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat shock proteins as biomarkers of lung cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020 Jun 2;21(6):477-485. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1736482. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32228356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doody JF, Wang Y, Patel SN, Joynes C, Lee SP, Gerlak J, Rolser RL, Li Y, Steiner P, Bassi R, et al. Inhibitory activity of cetuximab on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non.small cell lung cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:2642–2651. - PubMed
-
- Burtness B. The role of cetuximab in the treatment of squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005;5:1085–1093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
