Plumbagin inhibits tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer cells in vivo
- PMID: 22806981
- PMCID: PMC3496826
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.27724
Plumbagin inhibits tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer cells in vivo
Abstract
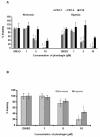
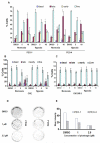
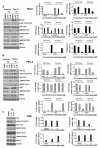
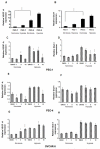
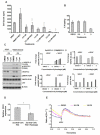
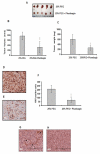
Angiogenesis is a hallmark of tumor development and metastatic progression, and anti-angiogenic drugs targeting the VEGF pathway have shown to decrease the disease progression in cancer patients. In this study, we have analyzed the anti-proliferative and anti-angiogenic property of plumbagin in cisplatin sensitive, BRCA2 deficient, PEO-1 and cisplatin resistant, BRCA2 proficient PEO-4 ovarian cancer cells. Both PEO-1 and PEO-4 ovarian cancer cells are sensitive to plumbagin irrespective of BRCA2 status in both normoxia and hypoxia. Importantly, plumbagin treatment effectively inhibits VEGF-A and Glut-1 in PEO-1 and PEO-4 ovarian cancer cells. We have also analyzed the p53 mutant, cisplatin resistant, and BRCA2 proficient OVCAR-5 cells. Plumbagin challenge also restricts the VEGF induced pro-angiogenic signaling in HUVECs and subsequently endothelial cell proliferation. In addition, we observe a significant effect on tumor regression among OVCAR-5 tumor-bearing mice treated with plumbagin, which is associated with significant inhibition of Ki67 and vWF expressions. Plumbagin also significantly reduces CD31 expression in an ear angiogenesis assay. Collectively, our studies indicate that plumbagin, as an anti-cancer agent disrupts growth of ovarian cancer cells through the inhibition of proliferation as well as angiogenesis.
Copyright © 2012 UICC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plumbagin restrains hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis by suppressing the migration and invasion of tumor-derived vascular endothelial cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):15230-15241. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14774. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28122355 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin inhibits tumour angiogenesis and tumour growth through the Ras signalling pathway following activation of the VEGF receptor-2.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(4b):1084-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01532.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21658027 Free PMC article.
-
L-5F, an apolipoprotein A-I mimetic, inhibits tumor angiogenesis by suppressing VEGF/basic FGF signaling pathways.Integr Biol (Camb). 2011 Apr;3(4):479-89. doi: 10.1039/c0ib00147c. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Integr Biol (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21283904 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Pathways Involved in Tumor Angiogenesis and Bevacizumab Based Anti-Angiogenic Therapy with Special References to Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 14;18(9):1967. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091967. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28906427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The phytochemical plumbagin: mechanism behind its "pleiotropic" nature and potential as an anticancer treatment.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Nov;98(11):3585-3601. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03861-9. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39271481 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the Potential Role of Nanotechnology in Liver Fibrosis: A Paradigm in Therapeutics.Molecules. 2023 Mar 20;28(6):2811. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062811. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives on mechanistic implications of ROS inducers for targeting viral infections.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 5;890:173621. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173621. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33068588 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin inhibits tumor angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma in mice by modulating nuclear factor-kappa B pathway.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Feb;9(2):556-564. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.12.03. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117400 Free PMC article.
-
GAIP interacting protein C-terminus regulates autophagy and exosome biogenesis of pancreatic cancer through metabolic pathways.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 3;9(12):e114409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114409. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25469510 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal endophytes of Plumbago zeylanica L. enhances plumbagin content.Bot Stud. 2019 Sep 7;60(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40529-019-0270-1. Bot Stud. 2019. PMID: 31494810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Satchi-Fainaro R, Puder M, Davies JW, Tran HT, Sampson DA, Greene AK, Corfas G, Folkman J. Targeting angiogenesis with a conjugate of HPMA copolymer and TNP-470. Nat Med. 2004;10:255–61. - PubMed
-
- Maeda N, Matsubara K, Yoshida H, Mizushina Y. Anti-cancer effect of spinach glycoglycerolipids as angiogenesis inhibitors based on the selective inhibition of DNA polymerase activity. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011;11:32–8. - PubMed
-
- Mizushina Y, Saito A, Horikawa K, Nakajima N, Tanaka A, Yoshida H, Matsubara K. Acylated catechin derivatives: inhibitors of DNA polymerase and angiogenesis. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2011;3:1337–48. - PubMed
-
- Padhye S, Dandawate P, Yusufi M, Ahmad A, Sarkar FH. Perspectives on medicinal properties of plumbagin and its analogs. Med. Res. Rev. 2010 doi: 10.1002/med.20235. - PubMed
-
- Srinivas G, Annab LA, Gopinath G, Banerji A, Srinivas P. Antisense blocking of BRCA1 enhances sensitivity to plumbagin but not tamoxifen in BG-1 ovarian cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2004;39:15–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

