Antibodies to the central conserved region of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) G protein block RSV G protein CX3C-CX3CR1 binding and cross-neutralize RSV A and B strains
- PMID: 22551066
- PMCID: PMC3366338
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2011.0094
Antibodies to the central conserved region of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) G protein block RSV G protein CX3C-CX3CR1 binding and cross-neutralize RSV A and B strains
Abstract
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a primary cause of severe lower respiratory tract disease in infants, young children, and the elderly worldwide, and despite decades of effort, there remains no safe and effective vaccine. RSV modifies the host immune response during infection by CX3C chemokine mimicry adversely affecting pulmonary leukocyte chemotaxis and CX3CR1+ RSV-specific T-cell responses. In this study we investigated whether immunization of mice with RSV G protein polypeptides from strain A2 could induce antibodies that block G protein-CX3CR1 interactions of both RSV A and B strains. The results show that mice immunized with RSV A2 G polypeptides generate antibodies that block binding of RSV A2 and B1 native G proteins to CX3CR1, and that these antibodies effectively cross-neutralize both A and B strains of RSV. These findings suggest that vaccines that induce RSV G protein-CX3CR1 blocking antibodies may provide a disease intervention strategy in the efforts to develop safe and efficacious RSV vaccines.
Figures

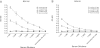
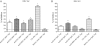
Similar articles
-
Vaccination to induce antibodies blocking the CX3C-CX3CR1 interaction of respiratory syncytial virus G protein reduces pulmonary inflammation and virus replication in mice.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(2):1148-57. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01755-09. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19864390 Free PMC article.
-
Mutating the CX3C Motif in the G Protein Should Make a Live Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Safer and More Effective.J Virol. 2017 Apr 28;91(10):e02059-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02059-16. Print 2017 May 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28275196 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) G Protein Vaccines With Central Conserved Domain Mutations Induce CX3C-CX3CR1 Blocking Antibodies.Viruses. 2021 Feb 23;13(2):352. doi: 10.3390/v13020352. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33672319 Free PMC article.
-
The role of respiratory syncytial virus G protein in immune cell infection and pathogenesis.EBioMedicine. 2024 Sep;107:105318. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105318. Epub 2024 Aug 31. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39217853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human respiratory syncytial virus: pathogenesis, immune responses, and current vaccine approaches.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Oct;37(10):1817-1827. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3289-4. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29876771 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenicity and inflammatory properties of respiratory syncytial virus attachment G protein in cotton rats.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 18;16(2):e0246770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246770. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33600439 Free PMC article.
-
Nonglycosylated G-Protein Vaccine Protects against Homologous and Heterologous Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Challenge, while Glycosylated G Enhances RSV Lung Pathology and Cytokine Levels.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(16):8193-205. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00133-15. Epub 2015 May 27. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26018164 Free PMC article.
-
Novel antigens for RSV vaccines.Curr Opin Immunol. 2015 Aug;35:30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.04.005. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26070108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) G monoclonal antibodies reduce lung inflammation and viral lung titers when delivered therapeutically in a BALB/c mouse model.Antiviral Res. 2018 Jun;154:149-157. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.04.014. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 29678551 Free PMC article.
-
CX3CR1 Is a Receptor for Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Cotton Rats.J Virol. 2021 Jul 26;95(16):e0001021. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00010-21. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34037420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amanatidou V. Sourvinos G. Apostolakis S. Tsilimigaki A. Spandidos DA. T280M variation of the CX3C receptor gene is associated with increased risk for severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Pediatric Infect Dis J. 2006;25:410–414. - PubMed
-
- Anderson LJ. Hierholzer JC. Tsou C. Hendry RM. Fernie BF. Stone Y. McIntosh K. Antigenic characterization of respiratory syncytial virus strains with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:626–633. - PubMed
-
- Arnold R. Konig B. Werchau H. Konig W. Respiratory syncytial virus deficient in soluble G protein induced an increased proinflammatory response in human lung epithelial cells. Virology. 2004;330:384–397. - PubMed
-
- Beck A. Klinguer-Hamour C. Bussat MC, et al. Peptides as tools and drugs for immunotherapies. J Peptide Sci. 2007;13:588–602. - PubMed
-
- Belshe RB. Anderson EL. Walsh EE. Immunogenicity of purified F glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus: clinical and immune responses to subsequent natural infection in children. J Infect Dis. 1993;168:1024–1029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

