Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus interacts with EphrinA2 receptor to amplify signaling essential for productive infection
- PMID: 22509030
- PMCID: PMC3358903
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1119592109
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus interacts with EphrinA2 receptor to amplify signaling essential for productive infection
Abstract
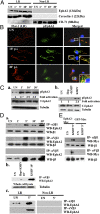
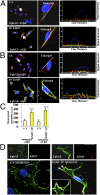
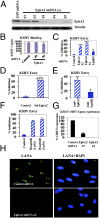
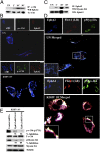
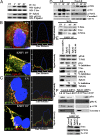
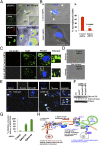
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), etiologically associated with Kaposi's sarcoma, uses integrins (α3β1, αVβ3, and αVβ5) and associated signaling to enter human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC-d), an in vivo target of infection. KSHV infection activated c-Cbl, which induced the selective translocation of KSHV into lipid rafts (LRs) along with the α3β1, αVβ3, and xCT receptors, but not αVβ5. LR-translocated receptors were monoubiquitinated, leading to productive macropinocytic entry, whereas non-LR-associated αVβ5 was polyubiquitinated, leading to clathrin-mediated entry that was targeted to lysosomes. Because the molecule(s) that integrate signal pathways and productive KSHV macropinocytosis were unknown, we immunoprecipitated KSHV-infected LR fractions with anti-α3β1 antibodies and analyzed them by mass spectrometry. The tyrosine kinase EphrinA2 (EphA2), implicated in many cancers, was identified in this analysis. EphA2 was activated by KSHV. EphA2 was also associated with KSHV and integrins (α3β1 and αVβ3) in LRs early during infection. Preincubation of virus with soluble EphA2, knockdown of EphA2 by shRNAs, or pretreatment of cells with anti-EphA2 monoclonal antibodies or tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib significantly reduced KSHV entry and gene expression. EphA2 associates with c-Cbl-myosin IIA and augmented KSHV-induced Src and PI3-K signals in LRs, leading to bleb formation and macropinocytosis of KSHV. EphA2 shRNA ablated macropinocytosis-associated signaling events, virus internalization, and productive nuclear trafficking of KSHV DNA. Taken together, these studies demonstrate that the EphA2 receptor acts as a master assembly regulator of KSHV-induced signal molecules and KSHV entry in endothelial cells and suggest that the EphA2 receptor is an attractive target for controlling KSHV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CIB1 synergizes with EphrinA2 to regulate Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus macropinocytic entry in human microvascular dermal endothelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 13;10(2):e1003941. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003941. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24550731 Free PMC article.
-
c-Cbl-mediated selective virus-receptor translocations into lipid rafts regulate productive Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection in endothelial cells.J Virol. 2011 Dec;85(23):12410-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05953-11. Epub 2011 Sep 21. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21937638 Free PMC article.
-
p130Cas scaffolds the signalosome to direct adaptor-effector cross talk during Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus trafficking in human microvascular dermal endothelial cells.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(23):13858-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01674-14. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25253349 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the Roles of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase c-Cbl, ESCRT Machinery, and Host Cell Signaling in Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Entry and Trafficking.J Virol. 2018 Jan 30;92(4):e01376-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01376-17. Print 2018 Feb 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29167336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KSHV Entry and Trafficking in Target Cells-Hijacking of Cell Signal Pathways, Actin and Membrane Dynamics.Viruses. 2016 Nov 14;8(11):305. doi: 10.3390/v8110305. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27854239 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploitation of Cellular Cytoskeletons and Signaling Pathways for Cell Entry by Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and the Closely Related Rhesus Rhadinovirus.Pathogens. 2012 Dec;1(2):102-27. doi: 10.3390/pathogens1020102. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Pathogens. 2012. PMID: 23420076 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 inhibitors are efficacious against Kaposi Sarcoma by enhancing the degradation of the essential viral gene LANA, of the viral co-receptor EphA2 as well as other client proteins.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(11):e1003048. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003048. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23209418 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Host Tyrosine Kinase Receptor EPHA2 Signaling Affects Uropathogen Infection in Human Bladder Epithelial Cells.Pathogens. 2022 Oct 12;11(10):1176. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11101176. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36297233 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Host Cellular Factors as a Strategy of Therapeutic Intervention for Herpesvirus Infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Mar 19;11:603309. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.603309. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33816328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CIB1 synergizes with EphrinA2 to regulate Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus macropinocytic entry in human microvascular dermal endothelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 13;10(2):e1003941. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003941. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24550731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang Y, et al. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865–1869. - PubMed
-
- Ganem D. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. In: Knipe DM, et al., editors. Fields Virology. 5th Ed. Vol 2. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2875–2888.
-
- Akula SM, Pramod NP, Wang FZ, Chandran B. Integrin alpha3beta1 (CD 49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) entry into the target cells. Cell. 2002;108:407–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

