Immune response to bacteria induces dissemination of Ras-activated Drosophila hindgut cells
- PMID: 22498775
- PMCID: PMC3367237
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.44
Immune response to bacteria induces dissemination of Ras-activated Drosophila hindgut cells
Abstract
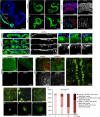
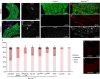
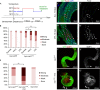
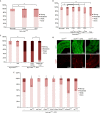
Although pathogenic bacteria are suspected contributors to colorectal cancer progression, cancer-promoting bacteria and their mode of action remain largely unknown. Here we report that sustained infection with the human intestinal colonizer Pseudomonas aeruginosa synergizes with the Ras1V12 oncogene to induce basal invasion and dissemination of hindgut cells to distant sites. Cross-talk between infection and dissemination requires sustained activation by the bacteria of the Imd-dTab2-dTak1 innate immune pathway, which converges with Ras1V12 signalling on JNK pathway activation, culminating in extracellular matrix degradation. Hindgut, but not midgut, cells are amenable to this cooperative dissemination, which is progressive and genetically and pharmacologically inhibitable. Thus, Drosophila hindgut provides a valuable system for the study of intestinal malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ras-oncogenic Drosophila hindgut but not midgut cells use an inflammation-like program to disseminate to distant sites.Gut Microbes. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):54-9. doi: 10.4161/gmic.22429. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Gut Microbes. 2013. PMID: 23060054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila TAB2 is required for the immune activation of JNK and NF-kappaB.Cell Signal. 2006 Jul;18(7):964-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.08.020. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 16311020
-
Synergy between bacterial infection and genetic predisposition in intestinal dysplasia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Dec 8;106(49):20883-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911797106. Epub 2009 Nov 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19934041 Free PMC article.
-
In Drosophila, RhoGEF2 cooperates with activated Ras in tumorigenesis through a pathway involving Rho1-Rok-Myosin-II and JNK signalling.Dis Model Mech. 2013 May;6(3):661-78. doi: 10.1242/dmm.010066. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 23324326 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of immune recognition and response in Drosophila host defense.Adv Genet. 2013;83:71-97. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407675-4.00002-X. Adv Genet. 2013. PMID: 23890212 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Sequencing-Based Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Regulatory Mechanism of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) Nymph Parasitized by Encarsia sophia (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae).PLoS One. 2016 Jun 22;11(6):e0157684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157684. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27332546 Free PMC article.
-
Constructing personalized longitudinal holo'omes of colon cancer-prone humans and their modeling in flies and mice.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 4;10(41):4224-4246. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6463. eCollection 2019 Jun 25. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 31289620 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila melanogaster: a first step and a stepping-stone to anti-infectives.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;13(5):763-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23992884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional exploration of colorectal cancer genomes using Drosophila.Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 29;7:13615. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13615. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27897178 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of intestinal Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients with cancer.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Jan 7;3:115. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00115. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24432250 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ellmerich S, Scholler M, Duranton B, Gosse F, Galluser M, Klein JP, Raul F (2000) Promotion of intestinal carcinogenesis by Streptococcus bovis. Carcinogenesis 21: 753–756 - PubMed
-
- Guarino M, Rubino B, Ballabio G (2007) The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology. Pathology 39: 305–318 - PubMed
-
- Voulgari A, Pintzas A (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms, markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic. Biochim Biophys Acta 1796: 75–90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

