Spinal 12-lipoxygenase-derived hepoxilin A3 contributes to inflammatory hyperalgesia via activation of TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors
- PMID: 22493235
- PMCID: PMC3340022
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1110460109
Spinal 12-lipoxygenase-derived hepoxilin A3 contributes to inflammatory hyperalgesia via activation of TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors
Abstract
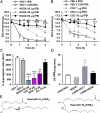
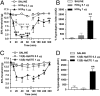
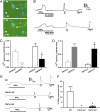
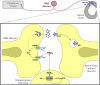
Peripheral inflammation initiates changes in spinal nociceptive processing leading to hyperalgesia. Previously, we demonstrated that among 102 lipid species detected by LC-MS/MS analysis in rat spinal cord, the most notable increases that occur after intraplantar carrageenan are metabolites of 12-lipoxygenases (12-LOX), particularly hepoxilins (HXA(3) and HXB(3)). Thus, we examined involvement of spinal LOX enzymes in inflammatory hyperalgesia. In the current work, we found that intrathecal (IT) delivery of the LOX inhibitor nordihydroguaiaretic acid prevented the carrageenan-evoked increase in spinal HXB(3) at doses that attenuated the associated hyperalgesia. Furthermore, IT delivery of inhibitors targeting 12-LOX (CDC, Baicalein), but not 5-LOX (Zileuton) dose-dependently attenuated tactile allodynia. Similarly, IT delivery of 12-LOX metabolites of arachidonic acid 12(S)-HpETE, 12(S)-HETE, HXA(3), or HXB(3) evoked profound, persistent tactile allodynia, but 12(S)-HpETE and HXA(3) produced relatively modest, transient heat hyperalgesia. The pronociceptive effect of HXA(3) correlated with enhanced release of Substance P from primary sensory afferents. Importantly, HXA(3) triggered sustained mobilization of calcium in cells stably overexpressing TRPV1 or TRPA1 receptors and in acutely dissociated rodent sensory neurons. Constitutive deletion or antagonists of TRPV1 (AMG9810) or TRPA1 (HC030031) attenuated this action. Furthermore, pretreatment with antihyperalgesic doses of AMG9810 or HC030031 reduced spinal HXA(3)-evoked allodynia. These data indicate that spinal HXA(3) is increased by peripheral inflammation and promotes initiation of facilitated nociceptive processing through direct activation of TRPV1 and TRPA1 at central terminals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
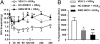
Similar articles
-
Systematic analysis of rat 12/15-lipoxygenase enzymes reveals critical role for spinal eLOX3 hepoxilin synthase activity in inflammatory hyperalgesia.FASEB J. 2013 May;27(5):1939-49. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-217414. Epub 2013 Feb 4. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23382512 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of spinal 15-LOX-1 attenuates TLR4-dependent, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-unresponsive hyperalgesia in male rats.Pain. 2018 Dec;159(12):2620-2629. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001373. Pain. 2018. PMID: 30130298 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of hepoxilins: evidence for the presence of a hepoxilin synthase activity in rat insulinoma cells.FEBS Lett. 2003 Mar 13;538(1-3):107-12. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00151-0. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12633862
-
Structure, biochemistry and biology of hepoxilins: an update.FEBS J. 2007 Jul;274(14):3503-3512. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05910.x. Epub 2007 Jul 2. FEBS J. 2007. PMID: 17608719 Review.
-
[Activation and regulation of nociceptive transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, TRPV1 and TRPA1].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Mar;130(3):289-94. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.289. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20190512 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Hydroxy-epoxide and keto-epoxide derivatives of linoleic acid activate trigeminal neurons.Neurobiol Pain. 2020 Apr 30;7:100046. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2020.100046. eCollection 2020 Jan-Jul. Neurobiol Pain. 2020. PMID: 32478201 Free PMC article.
-
Gallic acid functions as a TRPA1 antagonist with relevant antinociceptive and antiedematogenic effects in mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;387(7):679-89. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-0978-0. Epub 2014 Apr 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24722818
-
A review of non-prostanoid, eicosanoid receptors: expression, characterization, regulation, and mechanism of action.J Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Mar;16(1):5-46. doi: 10.1007/s12079-021-00630-6. Epub 2021 Jun 26. J Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 34173964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depolarizing Effectors of Bradykinin Signaling in Nociceptor Excitation in Pain Perception.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018 May 1;26(3):255-267. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2017.127. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018. PMID: 29378387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroinflammation in the Dorsal Root Ganglia and Dorsal Horn Contributes to Persistence of Nociceptor Sensitization in SIV-Infected Antiretroviral Therapy-Treated Macaques.Am J Pathol. 2023 Dec;193(12):2017-2030. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.08.014. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Am J Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37734588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dirig DM, Isakson PC, Yaksh TL. Effect of COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition on induction and maintenance of carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;285:1031–1038. - PubMed
-
- Malmberg AB, Yaksh TL. Hyperalgesia mediated by spinal glutamate or substance P receptor blocked by spinal cyclooxygenase inhibition. Science. 1992;257:1276–1279. - PubMed
-
- Jain NK, Kulkarni SK, Singh A. Role of cysteinyl leukotrienes in nociceptive and inflammatory conditions in experimental animals. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;423:85–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

