Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline
- PMID: 22476197
- PMCID: PMC3314463
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI59903
Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline
Abstract
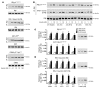
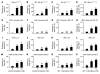
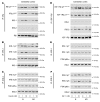
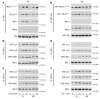
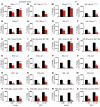
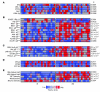
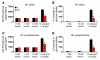
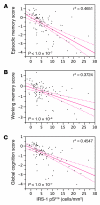
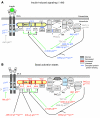
While a potential causal factor in Alzheimer's disease (AD), brain insulin resistance has not been demonstrated directly in that disorder. We provide such a demonstration here by showing that the hippocampal formation (HF) and, to a lesser degree, the cerebellar cortex in AD cases without diabetes exhibit markedly reduced responses to insulin signaling in the IR→IRS-1→PI3K signaling pathway with greatly reduced responses to IGF-1 in the IGF-1R→IRS-2→PI3K signaling pathway. Reduced insulin responses were maximal at the level of IRS-1 and were consistently associated with basal elevations in IRS-1 phosphorylated at serine 616 (IRS-1 pS⁶¹⁶) and IRS-1 pS⁶³⁶/⁶³⁹. In the HF, these candidate biomarkers of brain insulin resistance increased commonly and progressively from normal cases to mild cognitively impaired cases to AD cases regardless of diabetes or APOE ε4 status. Levels of IRS-1 pS⁶¹⁶ and IRS-1 pS⁶³⁶/⁶³⁹ and their activated kinases correlated positively with those of oligomeric Aβ plaques and were negatively associated with episodic and working memory, even after adjusting for Aβ plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and APOE ε4. Brain insulin resistance thus appears to be an early and common feature of AD, a phenomenon accompanied by IGF-1 resistance and closely associated with IRS-1 dysfunction potentially triggered by Aβ oligomers and yet promoting cognitive decline independent of classic AD pathology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Alzheimer’s disease: the new promise.J Clin Invest. 2012 Apr;122(4):1191. doi: 10.1172/jci62745. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22754953 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer's disease- associated Aβ oligomers.J Clin Invest. 2012 Apr;122(4):1339-53. doi: 10.1172/JCI57256. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22476196 Free PMC article.
-
Defects in IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor and IRS-1/2 in Alzheimer's disease indicate possible resistance to IGF-1 and insulin signalling.Neurobiol Aging. 2010 Feb;31(2):224-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.04.002. Neurobiol Aging. 2010. PMID: 18479783
-
The role of neuronal insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: possible therapeutic implications.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014 Mar;13(2):322-37. doi: 10.2174/18715273113126660141. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24059318 Review.
-
Neuronal IGF-1 resistance reduces Abeta accumulation and protects against premature death in a model of Alzheimer's disease.FASEB J. 2009 Oct;23(10):3315-24. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-132043. Epub 2009 Jun 1. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19487308
-
Decoding Alzheimer's disease from perturbed cerebral glucose metabolism: implications for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Sep;108:21-43. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23850509 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired glucose tolerance in midlife and longitudinal changes in brain function during aging.Neurobiol Aging. 2013 Oct;34(10):2271-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.03.025. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Neurobiol Aging. 2013. PMID: 23608110 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal DNA damage response-associated dysregulation of signalling pathways and cholesterol metabolism at the earliest stages of Alzheimer-type pathology.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2016 Feb;42(2):167-79. doi: 10.1111/nan.12252. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26095650 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal human BACE1 knockin induces systemic diabetes in mice.Diabetologia. 2016 Jul;59(7):1513-1523. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3960-1. Epub 2016 May 2. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27138913 Free PMC article.
-
The Future of Incretin-Based Approaches for Neurodegenerative Diseases in Older Adults: Which to Choose? A Review of their Potential Efficacy and Suitability.Drugs Aging. 2021 May;38(5):355-373. doi: 10.1007/s40266-021-00853-7. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Drugs Aging. 2021. PMID: 33738783 Review.
-
Can insulin signaling pathways be targeted to transport Aβ out of the brain?Front Aging Neurosci. 2015 Jun 16;7:114. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00114. eCollection 2015. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26136681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goldstein BJ. Insulin resistance as the core defect in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90(5A):3G–10G. - PubMed
-
- Zhao W-Q, Townsend M. Insulin resistance and amyloidogenesis as common molecular foundation for type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(5):482–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

