Klotho-beta overexpression as a novel target for suppressing proliferation and fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 22439738
- PMCID: PMC3361496
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-14
Klotho-beta overexpression as a novel target for suppressing proliferation and fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: We had previously demonstrated overexpression of fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 (FGFR4) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, additional molecular mechanisms resulting in amplified FGFR4 signaling in HCC remain under-studied. Here, we studied the mechanistic role of its co-receptor klotho-beta (KLB) in driving elevated FGFR4 activity in HCC progression.
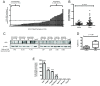
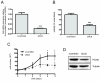
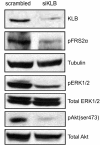
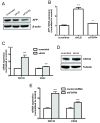
Results: Quantitative real-time PCR analysis identified frequent elevation of KLB gene expression in HCC tumors relative to matched non-tumor tissue, with a more than two-fold increase correlating with development of multiple tumors in patients. KLB-silencing in Huh7 cells decreased cell proliferation and suppressed FGFR4 downstream signaling. While transient repression of KLB-FGFR4 signaling decreased protein expression of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a HCC diagnostic marker, prolonged inhibition enriched for resistant HCC cells exhibiting increased liver stemness.
Conclusions: Elevated KLB expression in HCC tissues provides further credence to the oncogenic role of increased FGFR4 signaling in HCC progression and represents a novel biomarker to identify additional patients amenable to anti-FGFR4 therapy. The restricted tissue expression profile of KLB, together with the anti-proliferative effect observed with KLB-silencing, also qualifies it as a specific and potent therapeutic target for HCC patients. The enrichment of a liver stem cell-like population in response to extended KLB-FGFR4 repression necessitates further investigation to target the development of drug resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FGFR redundancy limits the efficacy of FGFR4-selective inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 4;119(40):e2208844119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208844119. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36179047 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 regulates proliferation, anti-apoptosis and alpha-fetoprotein secretion during hepatocellular carcinoma progression and represents a potential target for therapeutic intervention.J Hepatol. 2009 Jan;50(1):118-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.08.015. Epub 2008 Oct 12. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19008009
-
Klotho-beta and fibroblast growth factor 19 expression correlates with early recurrence of resectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Int. 2019 Sep;39(9):1682-1691. doi: 10.1111/liv.14055. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Liver Int. 2019. PMID: 30698907
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 15/19 in Hepatocarcinogenesis.Dig Dis. 2017;35(3):158-165. doi: 10.1159/000450905. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Dig Dis. 2017. PMID: 28249259 Review.
-
FGF19-FGFR4 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2019 Jun 4;8(6):536. doi: 10.3390/cells8060536. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31167419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Is fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 a suitable target of cancer therapy?Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(17):2881-98. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990594. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23944363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum β-klotho is a potential biomarker in the prediction of clinical outcomes among patients with NSCLC.J Thorac Dis. 2021 May;13(5):3137-3150. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-798. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 34164204 Free PMC article.
-
Role of FGF15 in Hepatic Surgery in the Presence of Tumorigenesis: Dr. Jekyll or Mr. Hyde?Cells. 2021 Jun 7;10(6):1421. doi: 10.3390/cells10061421. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34200439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gamma-Klotho exhibits multiple roles in tumor growth of human bladder cancer.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 13;9(28):19508-19524. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24628. eCollection 2018 Apr 13. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29731962 Free PMC article.
-
Benzylidene-indolinones are effective as multi-targeted kinase inhibitor therapeutics against hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Oncol. 2014 Oct;8(7):1266-77. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2014.04.008. Epub 2014 May 2. Mol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24839937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ye QH, Qin LX, Forgues M, He P, Kim JW, Peng AC, Simon R, Li Y, Robles AI, Chen Y. et al.Predicting hepatitis B virus-positive metastatic hepatocellular carcinomas using gene expression profiling and supervised machine learning. NatMed. 2003;9(4):416–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

