The viral and cellular microRNA targetome in lymphoblastoid cell lines
- PMID: 22291592
- PMCID: PMC3266933
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002484
The viral and cellular microRNA targetome in lymphoblastoid cell lines
Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a ubiquitous human herpesvirus linked to a number of B cell cancers and lymphoproliferative disorders. During latent infection, EBV expresses 25 viral pre-microRNAs (miRNAs) and induces the expression of specific host miRNAs, such as miR-155 and miR-21, which potentially play a role in viral oncogenesis. To date, only a limited number of EBV miRNA targets have been identified; thus, the role of EBV miRNAs in viral pathogenesis and/or lymphomagenesis is not well defined. Here, we used photoactivatable ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (PAR-CLIP) combined with deep sequencing and computational analysis to comprehensively examine the viral and cellular miRNA targetome in EBV strain B95-8-infected lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs). We identified 7,827 miRNA-interaction sites in 3,492 cellular 3'UTRs. 531 of these sites contained seed matches to viral miRNAs. 24 PAR-CLIP-identified miRNA:3'UTR interactions were confirmed by reporter assays. Our results reveal that EBV miRNAs predominantly target cellular transcripts during latent infection, thereby manipulating the host environment. Furthermore, targets of EBV miRNAs are involved in multiple cellular processes that are directly relevant to viral infection, including innate immunity, cell survival, and cell proliferation. Finally, we present evidence that myc-regulated host miRNAs from the miR-17/92 cluster can regulate latent viral gene expression. This comprehensive survey of the miRNA targetome in EBV-infected B cells represents a key step towards defining the functions of EBV-encoded miRNAs, and potentially, identifying novel therapeutic targets for EBV-associated malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
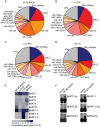
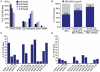
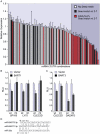
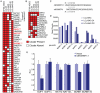
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus reactivation induces divergent abortive, reprogrammed, and host shutoff states by lytic progression.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 24;20(10):e1012341. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012341. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39446925 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus protein EBNA-LP engages YY1 through leucine-rich motifs to promote naïve B cell transformation.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jul 31;20(7):e1011950. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011950. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39083560 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Related Lymphoproliferative Disorders in Ataxia Telangiectasia: Does ATM Regulate EBV Life Cycle?Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 4;9:3060. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03060. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30662441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymerase theta is a synthetic lethal target for killing Epstein-Barr virus lymphomas.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0057224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00572-24. Epub 2024 Jun 11. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38860782 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
The presence of Epstein-Barr virus significantly impacts the transcriptional profile in immunodeficiency-associated Burkitt lymphoma.Front Microbiol. 2015 Jun 10;6:556. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00556. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26113842 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational inactivation of herpes simplex virus 1 microRNAs identifies viral mRNA targets and reveals phenotypic effects in culture.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(12):6589-603. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00504-13. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23536669 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular signature of Epstein Barr virus-positive Burkitt lymphoma and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder suggest different roles for Epstein Barr virus.Front Microbiol. 2014 Dec 23;5:728. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00728. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25566237 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus RNA functionally sequesters miR-122.Cell. 2015 Mar 12;160(6):1099-110. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.025. Cell. 2015. PMID: 25768906 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus as a potentiator of autoimmune diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 Nov;20(11):729-740. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01167-9. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39390260 Review.
References
-
- Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE, editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2655–2700.
-
- Pfeffer S, Zavolan M, Grasser FA, Chien M, Russo JJ, et al. Identification of virus-encoded microRNAs. Science. 2004;304:734–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

