Functional characterization and analgesic effects of mixed cannabinoid receptor/T-type channel ligands
- PMID: 22093952
- PMCID: PMC3250956
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-89
Functional characterization and analgesic effects of mixed cannabinoid receptor/T-type channel ligands
Abstract
Background: Both T-type calcium channels and cannabinoid receptors modulate signalling in the primary afferent pain pathway. Here, we investigate the analgesics activities of a series of novel cannabinoid receptor ligands with T-type calcium channel blocking activity.
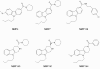
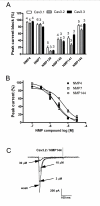
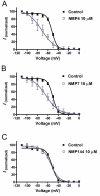
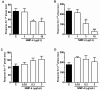
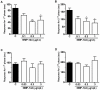
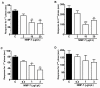
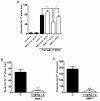
Results: Novel compounds were characterized in radioligand binding assays and in vitro functional assays at human and rat CB1 and CB2 receptors. The inhibitory effects of these compounds on transient expressed human T-type calcium channels were examined in tsA-201 cells using standard whole-cell voltage clamp techniques, and their analgesic effects in response to various administration routes (intrathecally, intraplantarly, intraperitoneally) assessed in the formalin model. A series of compounds were synthesized and evaluated for channel and receptor activity. Compound NMP-7 acted as non-selective CB1/CB2 agonist while NMP4 was found to be a CB1 partial agonist and CB2 inverse agonist. Furthermore, NMP-144 behaved as a selective CB2 inverse agonist. All of these three compounds completely inhibited peak Cav3.2 currents with IC50 values in the low micromolar range. All compounds mediated analgesic effects in the formalin model, but depending on the route of administration, could differentially affect phase 1 and phase 2 of the formalin response.
Conclusions: Our results reveal that a set of novel cannabinioid receptor ligands potently inhibit T-type calcium channels and show analgesic effects in vivo. Our findings suggest possible novel means of mediating pain relief through mixed T-type/cannabinoid receptor ligands.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analgesic effect of a mixed T-type channel inhibitor/CB2 receptor agonist.Mol Pain. 2013 Jul 1;9:32. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-9-32. Mol Pain. 2013. PMID: 23815854 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of novel cannabinoid based T-type calcium channel blockers with analgesic effects.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Feb 18;6(2):277-87. doi: 10.1021/cn500206a. Epub 2014 Nov 5. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25314588 Free PMC article.
-
NMP-7 inhibits chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain via block of Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels and activation of CB2 receptors.Mol Pain. 2014 Dec 6;10:77. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-10-77. Mol Pain. 2014. PMID: 25481027 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization of two novel selective cannabinoid CB(2) receptor inverse agonists.Pharmacol Res. 2010 Apr;61(4):349-54. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2009.11.011. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Pharmacol Res. 2010. PMID: 19961936
-
Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptor ligand specificity and the development of CB2-selective agonists.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(14):1428-43. doi: 10.2174/092986708784567716. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18537620 Review.
Cited by
-
Jekyll and Hide: The two faces of amyloid β.Commun Integr Biol. 2012 Sep 1;5(5):405-7. doi: 10.4161/cib.22571. Commun Integr Biol. 2012. PMID: 23181153 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathic pain; what we know and what we should do about it.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 22;4:1220034. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2023.1220034. eCollection 2023. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37810432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theoretical Study of the Structural Stability, Chemical Reactivity, and Protein Interaction for NMP Compounds as Modulators of the Endocannabinoid System.Molecules. 2022 Jan 9;27(2):414. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020414. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35056729 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the development of T-type calcium channel blockers for pain intervention.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;175(12):2375-2383. doi: 10.1111/bph.13906. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28608534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The terpenes camphene and alpha-bisabolol inhibit inflammatory and neuropathic pain via Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels.Mol Brain. 2021 Nov 14;14(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00876-6. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 34775970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pertwee RG, Howlett AC, Abood ME, Alexander SP, Di Marzo V, Elphick MR, Greasley PJ, Hansen HS, Kunos G, Mackie K. et al.International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: beyond CB and CB. Pharmacol Rev. 2010;62:588–631. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

