ncRNA- and Pc2 methylation-dependent gene relocation between nuclear structures mediates gene activation programs
- PMID: 22078878
- PMCID: PMC3297197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.054
ncRNA- and Pc2 methylation-dependent gene relocation between nuclear structures mediates gene activation programs
Erratum in
- Cell. 2013 Oct 10;155(2):478
Abstract
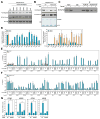
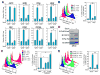
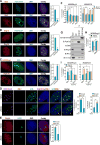
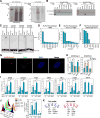
Although eukaryotic nuclei contain distinct architectural structures associated with noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), their potential relationship to regulated transcriptional programs remains poorly understood. Here, we report that methylation/demethylation of Polycomb 2 protein (Pc2) controls relocation of growth-control genes between Polycomb bodies (PcGs) and interchromatin granules (ICGs) in response to growth signals. This movement is the consequence of binding of methylated and unmethylated Pc2 to the ncRNAs TUG1 and MALAT1/NEAT2, located in PcGs and ICGs, respectively. These ncRNAs mediate assembly of multiple corepressors/coactivators and can serve to switch mark recognition by "readers" of the histone code. Additionally, binding of NEAT2 to unmethylated Pc2 promotes E2F1 SUMOylation, leading to activation of the growth-control gene program. These observations delineate a molecular pathway linking the actions of subnuclear structure-specific ncRNAs and nonhistone protein methylation to relocation of transcription units in the three-dimensional space of the nucleus, thus achieving coordinated gene expression programs.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Gene expression. An ncRNA relocation package.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Dec 14;13(1):1. doi: 10.1038/nrm3258. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22166993 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Pc2-mediated sumoylation of Smad-interacting protein 1 attenuates transcriptional repression of E-cadherin.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 21;280(42):35477-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504477200. Epub 2005 Aug 1. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16061479
-
Pc2 and SUMOylation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1401-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0351401. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031231 Review.
-
The polycomb protein Pc2 is a SUMO E3.Cell. 2003 Apr 4;113(1):127-37. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00159-4. Cell. 2003. PMID: 12679040
-
Selective interactions between vertebrate polycomb homologs and the SUV39H1 histone lysine methyltransferase suggest that histone H3-K9 methylation contributes to chromosomal targeting of Polycomb group proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Aug;22(15):5539-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5539-5553.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12101246 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin modifications by methylation and ubiquitination: implications in the regulation of gene expression.Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:243-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142422. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16756492 Review.
Cited by
-
Revisiting Epigenetics Fundamentals and Its Biomedical Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 19;25(14):7927. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147927. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M6A-mediated upregulation of lncRNA TUG1 in liver cancer cells regulates the antitumor response of CD8+ T cells and phagocytosis of macrophages.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(34):e2400695. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400695. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38981064 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1: Salt-Sensitive Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 18;25(10):5507. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105507. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs in skeletal development and disorders.Biol Res. 2024 Apr 22;57(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00497-y. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38644509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the defensive roles of lncRNAs during Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 22;15:1330660. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1330660. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38585701 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aagaard L, Laible G, Selenko P, Schmid M, Dorn R, Schotta G, Kuhfittig S, Wolf A, Lebersorger A, Singh PB, et al. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV-modifier Su(var)3-9 encode centromere-associated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. EMBO J. 1999;18:1923–1938. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A, Zink D, Becker PB. Chromodomains are protein-RNA interaction modules. Nature. 2000;407:405–409. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi S, Weinmann R, Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991;65:1063–1072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 DK039949-30/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477-37/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK018477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK74868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477-35/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097134/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065445-12/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868-05/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039949-17S1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA97134/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934-22/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065445/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK39949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934-23/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097134-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS34934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI_/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

