Neonatal Fc receptor and IgG-based therapeutics
- PMID: 22048693
- PMCID: PMC3225846
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.3.5.16983
Neonatal Fc receptor and IgG-based therapeutics
Abstract
The majority of potent new biologics today are IgG-based molecules that have demonstrated tissue-targeting specificity with favorable clinical response. Several factors determine the efficacy of these products, including target specificity, serum half-life and effector functions via complement-dependent cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity or drug conjugates. In this review, we will focus on the interaction between therapeutic antibody and neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), which is one of the critical factors in determining the circulating antibody half-life. Specifically, we will review the fundamental biology of FcRn, FcRn functions in various organs, Fc mutations designed to modulate binding to FcRn, IgG-based therapeutics that directly exploit FcRn functions and tools and strategies used to study FcRn-IgG interactions. Comprehensive understanding of FcRn-IgG interactions not only allows for development of effective therapeutics, but also avoidance of potential adverse effects.
Figures
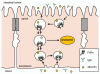
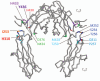
Similar articles
-
Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn): a novel target for therapeutic antibodies and antibody engineering.J Drug Target. 2014 May;22(4):269-78. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2013.875030. Epub 2014 Jan 9. J Drug Target. 2014. PMID: 24404896 Review.
-
Qualification of a homogeneous cell-based neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binding assay and its application to studies on Fc functionality of IgG-based therapeutics.J Immunol Methods. 2013 Apr 30;390(1-2):81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2013.01.011. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Immunol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23384837
-
The neonatal Fc receptor as therapeutic target in IgG-mediated autoimmune diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Aug;67(15):2533-50. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0318-6. Epub 2010 Mar 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20217455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering the Fc region of immunoglobulin G to modulate in vivo antibody levels.Nat Biotechnol. 2005 Oct;23(10):1283-8. doi: 10.1038/nbt1143. Epub 2005 Sep 25. Nat Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16186811
-
Importance of neonatal FcR in regulating the serum half-life of therapeutic proteins containing the Fc domain of human IgG1: a comparative study of the affinity of monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins to human neonatal FcR.J Immunol. 2010 Feb 15;184(4):1968-76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903296. Epub 2010 Jan 18. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20083659
Cited by
-
Fully human monoclonal antibody inhibitors of the neonatal fc receptor reduce circulating IgG in non-human primates.Front Immunol. 2015 Apr 23;6:176. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00176. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25954273 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of HL2351, a novel hybrid fc-fused interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, in healthy subjects: A first-in-human study.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;86(2):372-379. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14161. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31658396 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lack of ethnic differences in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of evolocumab between Caucasian and Asian populations.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;85(1):114-125. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13767. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30225890 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons for the clinic from rituximab pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.MAbs. 2013 Nov-Dec;5(6):826-37. doi: 10.4161/mabs.26008. Epub 2013 Aug 8. MAbs. 2013. PMID: 23933992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo fluorescence imaging of IgG1 aggregates after subcutaneous and intravenous injection in mice.Pharm Res. 2014 Jan;31(1):216-27. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1154-9. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 23949250
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
