Aurora-A inactivation causes mitotic spindle pole fragmentation by unbalancing microtubule-generated forces
- PMID: 22011530
- PMCID: PMC3226445
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-131
Aurora-A inactivation causes mitotic spindle pole fragmentation by unbalancing microtubule-generated forces
Abstract
Background: Aurora-A is an oncogenic kinase playing well-documented roles in mitotic spindle organisation. We previously found that Aurora-A inactivation yields the formation of spindles with fragmented poles that can drive chromosome mis-segregation. Here we have addressed the mechanism through which Aurora-A activity regulates the structure and cohesion of spindle poles.
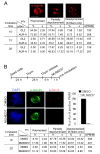
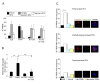
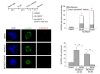
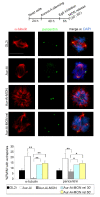
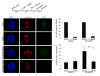
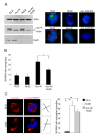
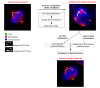
Results: We inactivated Aurora-A in human U2OS osteosarcoma cells either by RNA-interference-mediated silencing or treating cultures with the specific inhibitor MLN8237. We show that mitotic spindle pole fragmentation induced by Aurora-A inactivation is associated with microtubule hyperstabilisation. Silencing of the microtubule-stabilising factor ch-TOG prevents spindle pole fragmentation caused by inactivation of Aurora-A alone and concomitantly reduces the hyperstabilisation of microtubules. Furthermore, decreasing pole-directed spindle forces by inhibition of the Eg5 kinesin, or by destabilisation of microtubule-kinetochore attachments, also prevents pole fragmentation in Aurora-A-inactivated mitoses.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that microtubule-generated forces are imbalanced in Aurora-A-defective cells and exert abnormal pressure at the level of spindle poles, ultimately causing their fragmentation. This study therefore highlights a novel role of the Aurora-A kinase in regulating the balance between microtubule forces during bipolar spindle assembly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aurora-A and ch-TOG act in a common pathway in control of spindle pole integrity.Oncogene. 2008 Nov 20;27(51):6539-49. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.252. Epub 2008 Jul 28. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18663358
-
Roles of polo-like kinase 1 in the assembly of functional mitotic spindles.Curr Biol. 2004 Oct 5;14(19):1712-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.09.049. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15458642
-
Regulation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments by Aurora B kinase.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Oct;37(Pt 5):976-80. doi: 10.1042/BST0370976. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19754435 Review.
-
Aurora B phosphorylates centromeric MCAK and regulates its localization and microtubule depolymerization activity.Curr Biol. 2004 Feb 17;14(4):273-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.01.055. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 14972678
-
Detection and correction of merotelic kinetochore orientation by Aurora B and its partners.Cell Cycle. 2007 Jul 1;6(13):1558-64. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.13.4452. Epub 2007 May 18. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17603301 Review.
Cited by
-
The Aurora kinase A inhibitor TC-A2317 disrupts mitotic progression and inhibits cancer cell proliferation.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):84718-84735. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12448. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713168 Free PMC article.
-
Mitsui-7, heat-treated, and nitrogen-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes elicit genotoxicity in human lung epithelial cells.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2019 Oct 7;16(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12989-019-0318-0. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31590690 Free PMC article.
-
The RAL Enigma: Distinct Roles of RALA and RALB in Cancer.Cells. 2022 May 14;11(10):1645. doi: 10.3390/cells11101645. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35626682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of driver genes associated with chemotherapy resistance of Ewing's sarcoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Oct 15;11:6947-6956. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S172190. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30410352 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora A inhibition limits centrosome clustering and promotes mitotic catastrophe in cells with supernumerary centrosomes.Oncotarget. 2019 Feb 26;10(17):1649-1659. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26714. eCollection 2019 Feb 26. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 30899434 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

