Sirt1 enhances skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in mice during caloric restriction
- PMID: 21985785
- PMCID: PMC3204844
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI58554
Sirt1 enhances skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in mice during caloric restriction
Abstract
Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is a key component of the etiology of type 2 diabetes. Caloric restriction (CR) enhances the sensitivity of skeletal muscle to insulin. However, the molecular signals within skeletal muscle linking CR to improved insulin action remain largely unknown. Recently, the mammalian ortholog of Sir2, sirtuin 1 (Sirt1), has been identified as a potential transducer of perturbations in cellular energy flux into subsequent metabolic adaptations, including modulation of skeletal muscle insulin action. Here, we have demonstrated that CR increases Sirt1 deacetylase activity in skeletal muscle in mice, in parallel with enhanced insulin-stimulated phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling and glucose uptake. These adaptations in skeletal muscle insulin action were completely abrogated in mice lacking Sirt1 deacetylase activity. Mechanistically, Sirt1 was found to be required for the deacetylation and inactivation of the transcription factor Stat3 during CR, which resulted in decreased gene and protein expression of the p55α/p50α subunits of PI3K, thereby promoting more efficient PI3K signaling during insulin stimulation. Thus, these data demonstrate that Sirt1 is an integral signaling node in skeletal muscle linking CR to improved insulin action, primarily via modulation of PI3K signaling.
Figures
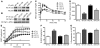

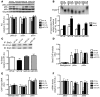
Similar articles
-
N1‑methylnicotinamide ameliorates insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic mice by activating the SIRT1/PGC‑1α signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Apr;23(4):270. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11909. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33576435
-
Neuronal Sirt1 deficiency increases insulin sensitivity in both brain and peripheral tissues.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10722-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.443606. Epub 2013 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23457303 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of AMP-activated protein kinase-α2 impairs the insulin-sensitizing effect of calorie restriction in skeletal muscle.Diabetes. 2012 May;61(5):1051-61. doi: 10.2337/db11-1180. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22396207 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of SIRT1 in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in skeletal muscle].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Jan 16;69:63-8. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1136379. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015. PMID: 25614674 Review. Polish.
-
Modulation of SIRT1-Foxo1 signaling axis by resveratrol: implications in skeletal muscle aging and insulin resistance.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(2):541-52. doi: 10.1159/000369718. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25612477 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolism, longevity and epigenetics.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 May;70(9):1525-41. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1295-3. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23467663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One-time injection of AAV8 encoding urocortin 2 provides long-term resolution of insulin resistance.JCI Insight. 2016 Sep 22;1(15):e88322. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.88322. JCI Insight. 2016. PMID: 27699250 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle-specific overexpression of SIRT1 does not enhance whole-body energy expenditure or insulin sensitivity in young mice.Diabetologia. 2013 Jul;56(7):1629-37. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2912-2. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23604553 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 regulates lamellipodium extension and migration of melanoma cells.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Jun;134(6):1693-1700. doi: 10.1038/jid.2014.50. Epub 2014 Jan 30. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24480879
-
Effects of Calorie Restriction and Fiber Type on Glucose Uptake and Abundance of Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation Proteins in Single Fibers from Old Rats.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017 Nov 9;72(12):1638-1646. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx099. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28531280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cartee GD, Kietzke EW, Briggs-Tung C. Adaptation of muscle glucose transport with caloric restriction in adult, middle-aged, and old rats. Am J Physiol. 1994;266(5 pt 2):R1443–R1447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD050837/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD012303-25/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR058878/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR058878-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD057022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024146/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007494/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

