Fetal growth restriction and the programming of heart growth and cardiac insulin-like growth factor 2 expression in the lamb
- PMID: 21807611
- PMCID: PMC3213418
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.211185
Fetal growth restriction and the programming of heart growth and cardiac insulin-like growth factor 2 expression in the lamb
Abstract
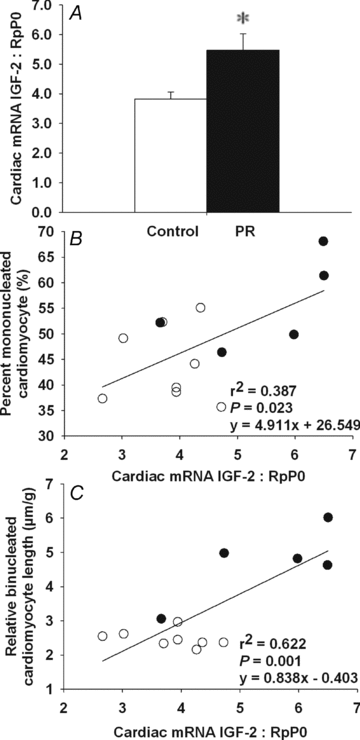
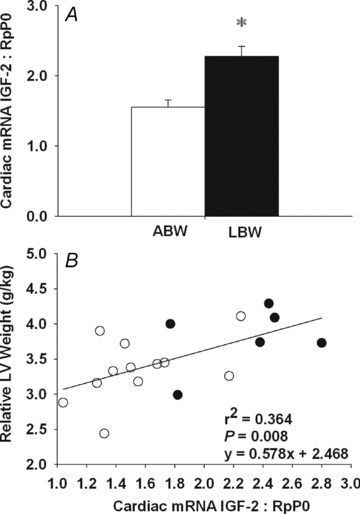
Reduced growth in fetal life together with accelerated growth in childhood, results in a ~50% greater risk of coronary heart disease in adult life. It is unclear why changes in patterns of body and heart growth in early life can lead to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in adulthood. We aimed to investigate the role of the insulin-like growth factors in heart growth in the growth-restricted fetus and lamb. Hearts were collected from control and placentally restricted (PR) fetuses at 137-144 days gestation and from average (ABW) and low (LBW) birth weight lambs at 21 days of age. We quantified cardiac mRNA expression of IGF-1, IGF-2 and their receptors, IGF-1R and IGF-2R, using real-time RT-PCR and protein expression of IGF-1R and IGF-2R using Western blotting. Combined bisulphite restriction analysis was used to assess DNA methylation in the differentially methylated region (DMR) of the IGF-2/H19 locus and of the IGF-2R gene. In PR fetal sheep, IGF-2, IGF-1R and IGF-2R mRNA expression was increased in the heart compared to controls. LBW lambs had a greater left ventricle weight relative to body weight as well as increased IGF-2 and IGF-2R mRNA expression in the heart, when compared to ABW lambs. No changes in the percentage of methylation of the DMRs of IGF-2/H19 or IGF-2R were found between PR and LBW when compared to their respective controls. In conclusion, a programmed increased in cardiac gene expression of IGF-2 and IGF-2R may represent an adaptive response to reduced substrate supply (e.g. glucose and/or oxygen) in order to maintain heart growth and may be the underlying cause for increased ventricular hypertrophy and the associated susceptibility of cardiomyocytes to ischaemic damage later in life.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IGF-2R-Gαq signaling and cardiac hypertrophy in the low-birth-weight lamb.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Apr 1;308(7):R627-35. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00346.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25632020 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal nutrient restriction during early to mid gestation up-regulates cardiac insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptors associated with enlarged ventricular size in fetal sheep.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2005 Aug;15(4):291-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2005.05.003. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2005. PMID: 16046163
-
IGF-2R-mediated signaling results in hypertrophy of cultured cardiomyocytes from fetal sheep.Biol Reprod. 2012 Jun 22;86(6):183. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.112.100388. Print 2012 Jun. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22441800
-
Early origins of heart disease: low birth weight and the role of the insulin-like growth factor system in cardiac hypertrophy.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012 Nov;39(11):958-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2012.05743.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22774980 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying insulin-like growth factor action: How mutations in the GH: IGF axis lead to short stature.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2011 Jun;8(4):374-81. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21972777 Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal undernutrition in late gestation increases IGF2 signalling molecules and collagen deposition in the right ventricle of the fetal sheep heart.J Physiol. 2018 Jun;596(12):2345-2358. doi: 10.1113/JP275806. Epub 2018 May 20. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29604078 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic hypoxemia in late gestation decreases cardiomyocyte number but does not change expression of hypoxia-responsive genes.J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Jul 28;3(4):e000531. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000531. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 25085511 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal dietary restriction during the periconceptional period in normal-weight or obese ewes results in adrenocortical hypertrophy, an up-regulation of the JAK/STAT and down-regulation of the IGF1R signaling pathways in the adrenal of the postnatal lamb.Endocrinology. 2013 Dec;154(12):4650-62. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1414. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 24108072 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The role of miRNA regulation in fetal cardiomyocytes, cardiac maturation and the risk of heart disease in adults.J Physiol. 2018 Dec;596(23):5625-5640. doi: 10.1113/JP276072. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29785790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA H19: A Novel Biomarker in Cardiovascular Disease.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2024 Mar;40(2):172-181. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202403_40(2).20230925A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38532821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barbera A, Giraud GD, Reller MD, Maylie J, Morton MJ, Thornburg KL. Right ventricular systolic pressure load alters myocyte maturation in fetal sheep. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000;279:R1157–R1164. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ, Eriksson JG, Forsen T, Osmond C. Fetal origins of adult disease: strength of effects and biological basis. Int J Epidemiol. 2002;31:1235–1239. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ, Osmond C, Forsen TJ, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG. Trajectories of growth among children who have coronary events as adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1802–1809. - PubMed
-
- Brown AL, Graham DE, Nissley SP, Hill DJ, Strain AJ, Rechler MM. Developmental regulation of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA in different rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:13144–13150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

