The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK and TNFα reduce renal klotho expression through NFκB
- PMID: 21719790
- PMCID: PMC3137579
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010101073
The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK and TNFα reduce renal klotho expression through NFκB
Abstract
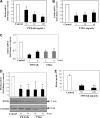
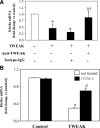
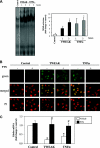
Proinflammatory cytokines contribute to renal injury, but the downstream effectors within kidney cells are not well understood. One candidate effector is Klotho, a protein expressed by renal cells that has antiaging properties; Klotho-deficient mice have an accelerated aging-like phenotype, including vascular injury and renal injury. Whether proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF and TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK), modulate Klotho is unknown. In mice, exogenous administration of TWEAK decreased expression of Klotho in the kidney. In the setting of acute kidney injury induced by folic acid, the blockade or absence of TWEAK abrogated the injury-related decrease in renal and plasma Klotho levels. TWEAK, TNFα, and siRNA-mediated knockdown of IκBα all activated NFκB and reduced Klotho expression in the MCT tubular cell line. Furthermore, inhibition of NFκB with parthenolide prevented TWEAK- or TNFα-induced downregulation of Klotho. Inhibition of histone deacetylase reversed TWEAK-induced downregulation of Klotho, and chromatin immunoprecipitation showed that TWEAK promotes RelA binding to the Klotho promoter, inducing its deacetylation. In conclusion, inflammatory cytokines, such as TWEAK and TNFα, downregulate Klotho expression through an NFκB-dependent mechanism. These results may partially explain the relationship between inflammation and diseases characterized by accelerated aging of organs, including CKD.
Copyright © 2011 by the American Society of Nephrology
Figures
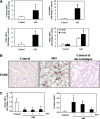
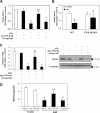
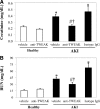
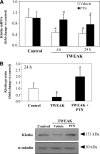
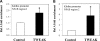
Similar articles
-
Bcl3: a regulator of NF-κB inducible by TWEAK in acute kidney injury with anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic properties in tubular cells.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Jul 7;49(7):e352. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.89. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28684863 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammatory cytokine TWEAK decreases PGC-1α expression and mitochondrial function in acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2016 Feb;89(2):399-410. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.332. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 26535995
-
TWEAK activates the non-canonical NFkappaB pathway in murine renal tubular cells: modulation of CCL21.PLoS One. 2010 Jan 29;5(1):e8955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008955. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20126461 Free PMC article.
-
Out of the TWEAKlight: Elucidating the Role of Fn14 and TWEAK in Acute Kidney Injury.Semin Nephrol. 2016 May;36(3):189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2016.03.006. Semin Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27339384 Review.
-
Downregulation of kidney protective factors by inflammation: role of transcription factors and epigenetic mechanisms.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):F1329-F1340. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00487.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27760772 Review.
Cited by
-
The association between the triglyceride-glucose index and serum anti-aging protein α- Klotho: a population-based study.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Nov 1;16(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01487-6. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39487503 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth-factor 23-Klotho axis is associated with systemic inflammation and myokine profile in children with chronic kidney disease.Hormones (Athens). 2024 Sep;23(3):517-526. doi: 10.1007/s42000-024-00586-3. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Hormones (Athens). 2024. PMID: 39112785
-
Tacrolimus Prevents TWEAK-Induced PLA2R Expression in Cultured Human Podocytes.J Clin Med. 2020 Jul 10;9(7):2178. doi: 10.3390/jcm9072178. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32664235 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of Klotho in clinical nephrology.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Jul;27(7):2650-7. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs160. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22802580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of fibroblast growth factor 23 and Klotho in uremic cardiomyopathy.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Jul;25(4):314-24. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000231. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27219043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P, Benigni A: Understanding the nature of renal disease progression. Kidney Int 51: 2–15, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ: The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology. Cell 104: 487–501, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Sanz AB, Sanchez-Nino MD, Ramos AM, Moreno JA, Santamaria B, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A: NF-kappaB in renal inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol 21: 1254–1262, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Ortiz A, Bustos C, Alonso J, Alcazar R, Lopez-Armada MJ, Plaza JJ, Gonzalez E, Egido J: Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the pathogenesis of experimental and human glomerulonephritis. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp 24: 53–77, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

