Retrotransposition of marked SVA elements by human L1s in cultured cells
- PMID: 21636526
- PMCID: PMC3153304
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddr245
Retrotransposition of marked SVA elements by human L1s in cultured cells
Abstract
Human retrotransposons generate structural variation and genomic diversity through ongoing retrotransposition and non-allelic homologous recombination. Cell culture retrotransposition assays have provided great insight into the genomic impact of retrotransposons, in particular, LINE-1(L1) and Alu elements; however, no such assay exists for the youngest active human retrotransposon, SINE-VNTR-Alu (SVA). Here we report the development of an SVA cell culture retrotransposition assay. We marked several SVAs with either neomycin or EGFP retrotransposition indicator cassettes. Engineered SVAs retrotranspose using L1 proteins supplemented in trans in multiple cell lines, including U2OS osteosarcoma cells where SVA retrotransposition is equal to that of an engineered L1. Engineered SVAs retrotranspose at 1-54 times the frequency of a marked pseudogene in HeLa HA cells. Furthermore, our data suggest a variable requirement for L1 ORF1p for SVA retrotransposition. Recovered engineered SVA insertions display all the hallmarks of LINE-1 retrotransposition and some contain 5' and 3' transductions, which are common for genomic SVAs. Of particular interest is the fact that four out of five insertions recovered from one SVA are full-length, with the 5' end of these insertions beginning within 5 nt of the CMV promoter transcriptional start site. This assay demonstrates that SVA elements are indeed mobilized in trans by L1. Previously intractable questions regarding SVA biology can now be addressed.
Figures
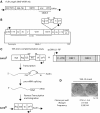

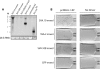
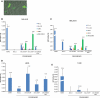

Similar articles
-
The non-autonomous retrotransposon SVA is trans-mobilized by the human LINE-1 protein machinery.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(4):1666-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr863. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22053090 Free PMC article.
-
The Engineered SVA Trans-mobilization Assay.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1400:203-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3372-3_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26895056
-
The minimal active human SVA retrotransposon requires only the 5'-hexamer and Alu-like domains.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Nov;32(22):4718-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00860-12. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23007156 Free PMC article.
-
SVA retrotransposons: Evolution and genetic instability.Semin Cancer Biol. 2010 Aug;20(4):234-45. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.04.001. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Semin Cancer Biol. 2010. PMID: 20416380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of Retroelements in Mammalian Gametes and Embryos.In Vivo. 2021 Jul-Aug;35(4):1921-1927. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12458. In Vivo. 2021. PMID: 34182464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Origin of a novel protein-coding gene family with similar signal sequence in Schistosoma japonicum.BMC Genomics. 2012 Jun 20;13:260. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-260. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22716200 Free PMC article.
-
Double strand break repair by capture of retrotransposon sequences and reverse-transcribed spliced mRNA sequences in mouse zygotes.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 28;5:12281. doi: 10.1038/srep12281. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26216318 Free PMC article.
-
Retrotransposon life cycle and its impacts on cellular responses.RNA Biol. 2024 Jan;21(1):11-27. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2409607. Epub 2024 Oct 13. RNA Biol. 2024. PMID: 39396200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing of transposable elements by the antiviral innate immune system.RNA. 2021 Apr 22;27(7):735-52. doi: 10.1261/rna.078721.121. Online ahead of print. RNA. 2021. PMID: 33888553 Free PMC article.
-
Enrichment of processed pseudogene transcripts in L1-ribonucleoprotein particles.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Sep 15;22(18):3730-48. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt225. Epub 2013 May 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23696454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lander E., Linton L., Birren B., Nusbaum C., Zody M., Baldwin J., Devon K., Dewar K., Doyle M., FitzHugh W. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. doi:10.1038/35057062. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cordaux R., Batzer M.A. The impact of retrotransposons on human genome evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009;10:691–703. doi:10.1038/nrg2640. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kazazian H.H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A.F., Phillips D.G., Antonarakis S.E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988;332:164–166. doi:10.1038/332164a0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wallace M.R., Andersen L.B., Saulino A.M., Gregory P.E., Glover T.W., Collins F.S. A de novo Alu insertion results in neurofibromatosis type 1. Nature. 1991;353:864–866. doi:10.1038/353864a0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ostertag E.M., Goodier J.L., Zhang Y., Kazazian H.H., Jr SVA elements are nonautonomous retrotransposons that cause disease in humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003;73:1444–1451. doi:10.1086/380207. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

