A patient with erythema nodosus leprosum and Chagas cardiopathy: challenges in patient management and review of the literature
- PMID: 21633036
- PMCID: PMC3110380
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.10-0547
A patient with erythema nodosus leprosum and Chagas cardiopathy: challenges in patient management and review of the literature
Abstract
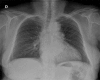
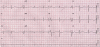
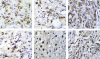
We report a patient with severe multi-bacillary leprosy complicated by recurrent episodes of erythema nodosum necrotisans that required thalidomide and/or corticosteroids during follow-up. Although the patient was from an area to which Chagas disease is endemic, this diagnosis was initially missed and was only investigated when heart failure developed in the patient. The difficulties of managing erythema nodosum necrotisans and heart failure concomitantly and those involved in excluding the diagnosis of acute myocarditis caused by reactivation of Chagas disease secondary to the immunosuppressive regimen are discussed. Other potential causes for the heart failure and possible interactions between the two diseases and their treatments are discussed. We also reviewed the literature for the association between leprosy and Chagas disease, both of which are highly endemic in Brazil. This case emphasizes the importance of searching for subclinical co-infections in leprosy patients because reactions frequently develop during specific treatment in these patients, and these reactions require prolonged therapy with immunosuppressive drugs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Bullous erythema nodosum leprosum. A case report in French Guiana].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1998 Mar;125(3):188-90. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1998. PMID: 9747246 French.
-
[Chemotherapy-induced erythema nodosum leprosum: successful treatment with thalidomide].Hautarzt. 2001 Oct;52(10 Pt 2):966-9. doi: 10.1007/s001050170009. Hautarzt. 2001. PMID: 11715395 German.
-
Erythema nodosum leprosum and HIV infection: A therapeutic experience.Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 2005 Sep;73(3):189-93. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 2005. PMID: 16830640
-
Potential of thalidomide and thalidomide analogues as immunomodulatory drugs in leprosy and leprosy reactions.Lepr Rev. 2000 Dec;71 Suppl:S117-20. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.20000082. Lepr Rev. 2000. PMID: 11201867 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Treatment of erythema nodosum leprosum using thalidomide].Acta Leprol. 1983 Jan-Mar;1(1):41-50. Acta Leprol. 1983. PMID: 6401140 Review. French. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Bacterial, fungal and parasitic co-infections in leprosy: A scoping review.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 May 22;17(5):e0011334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011334. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 37216331 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: COVID-19 and Chagas Disease in Two Coinfected Patients.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Dec;103(6):2353-2356. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-1185. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020. PMID: 33025877 Free PMC article.
-
Co-morbid infections in Hansen's disease patients in the United States: considerations for treatment.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013 Oct;89(4):781-3. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0167. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013. PMID: 23980128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global leprosy situation, World Health Organization Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2010;33:333–340.
-
- Bolletin de la Organizacion Panamericana de la Salud . Estimacion Cuantitativa de la Enfermedad de Chagas en las Americas. Montevideo, Uruguay: OPAS; 2006.
-
- Portal de Saúde. 2010. http://portal.saude.gov.br/portal/saude/profissional/area.cfm?id_area=1466 Available at. Accessed September 29.
-
- Ridley DS, Jopling WH. Classification of leprosy according to immunity: a five-group system. Int J Lepr. 1966;34:255–273. - PubMed
-
- Naafs B, Wheate HW. The time interval between the start of anti-leprosy treatment and the development of reactions in borderline patients. Lepr Rev. 1978;49:153–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

