Canonical NF-kappaB activation is essential for Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 TES2/CTAR2 gene regulation
- PMID: 21543491
- PMCID: PMC3126495
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00422-11
Canonical NF-kappaB activation is essential for Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 TES2/CTAR2 gene regulation
Abstract
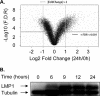
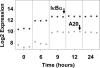
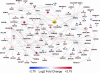
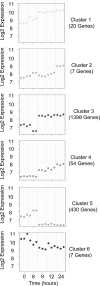
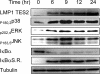
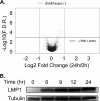
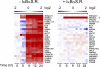
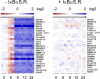
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) transforms rodent fibroblasts and is expressed in most EBV-associated malignancies. LMP1 (transformation effector site 2 [TES2]/C-terminal activation region 2 [CTAR2]) activates NF-κB, p38, Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) pathways. We have investigated LMP1 TES2 genome-wide RNA effects at 4 time points after LMP1 TES2 expression in HEK-293 cells. By using a false discovery rate (FDR) of <0.001 after correction for multiple hypotheses, LMP1 TES2 caused >2-fold changes in 1,916 mRNAs; 1,479 RNAs were upregulated and 437 were downregulated. In contrast to tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) stimulation, which transiently upregulates many target genes, LMP1 TES2 maintained most RNA effects through the time course, despite robust and sustained induction of negative feedback regulators, such as IκBα and A20. LMP1 TES2-regulated RNAs encode many NF-κB signaling proteins and secondary interacting proteins. Consequently, many LMP1 TES2-regulated RNAs encode proteins that form an extensive interactome. Gene set enrichment analyses found LMP1 TES2-upregulated genes to be significantly enriched for pathways in cancer, B- and T-cell receptor signaling, and Toll-like receptor signaling. Surprisingly, LMP1 TES2 and IκBα superrepressor coexpression decreased LMP1 TES2 RNA effects to only 5 RNAs, with FDRs of <0.001-fold and >2-fold changes. Thus, canonical NF-κB activation is critical for almost all LMP1 TES2 RNA effects in HEK-293 cells and a more significant therapeutic target than previously appreciated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates the JNK pathway through its extreme C terminus via a mechanism involving TRADD and TRAF2.J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1023-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1023-1035.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9882303 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein 1 TRAF-binding site induces NIK/IKK alpha-dependent noncanonical NF-kappaB activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):141-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2237183100. Epub 2003 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14691250 Free PMC article.
-
The residues between the two transformation effector sites of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 are not critical for B-lymphocyte growth transformation.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):9908-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.9908-9916.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559303 Free PMC article.
-
LMP1 TRAFficking activates growth and survival pathways.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;597:173-87. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-70630-6_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17633026 Review.
-
The Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:119-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428373 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and Emerging Functions of LRCH Proteins in Leukocyte Biology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 22;8:584134. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.584134. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33072765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus-Induced Metabolic Rearrangements in Human B-Cell Lymphomas.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jun 8;9:1233. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01233. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29937761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EBV-LMP1 induces APOBEC3s and mitochondrial DNA hypermutation in nasopharyngeal cancer.Cancer Med. 2020 Oct;9(20):7663-7671. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3357. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32815637 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines for Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Generation.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2349261. doi: 10.1155/2016/2349261. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27375745 Free PMC article.
-
E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Gammaherpesviruses and HIV: A Review of Virus Adaptation and Exploitation.Viruses. 2023 Sep 15;15(9):1935. doi: 10.3390/v15091935. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37766341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. 1988. Transformation of Balb 3T3 cells by the BNLF-1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene 2:461–467 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Baruch A. 2006. The multifaceted roles of chemokines in malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:357–371 - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B 57:289–300
-
- Ben Nasr H., et al. 2007. Association of IL-8 (-251)T/A polymorphism with susceptibility to and aggressiveness of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Hum. Immunol. 68:761–769 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

